It would be hard to find a company that doesn’t use computers or the internet. Naturally, cyber-attacks are a risk to almost all modern businesses. Therefore it’s important to have a security plan in place. Especially in a current climate when online attacks are on the rise.
A network security audit gives a good insight into a company’s security systems. Timely audit reports can indicate huge cybersecurity risks that, when patched, could improve an organization’s security state. In this article, we’ll present everything you should know about creating a network security audit checklist to help you improve your cybersecurity.
What is a network security audit?
A security audit evaluates all company’s network systems to eliminate potential security risks. Devices like servers, laptops, smartphones, and even virtual gateways should all be screened to ensure they’re safe to use. Generally, five different key areas must be checked:
Control implementation — based on the importance of the assets, various security controls have to be implemented to limit data exposure and restrict access.
Management practices — bad habits in cybersecurity management can severely backfire, so it’s essential to ensure that the processes use the best practices.
Network availability — all applications and data must be available for users immediately when needed.
Network security — computer networks with access to the internet serve as attack surfaces, so their security is central to the overall network security.
Overall performance — the general performance of an organization’s IT systems is a significant factor that, when resolved, could improve work performance.
Investigations of these areas and resolving found issues can drastically improve an organization’s security or performance.
Why do you need a network security audit checklist?
Current computer network systems can be so complex that the list of areas that must be supervised is quite extensive. Due to its scope, a network security audit checklist helps to make the audit easier by putting it in a systematic approach. It’s the easiest way to ensure that everything that should be secured is checked for issues.
While the checklist’s importance cannot be understated, it’s also important to realize that audits should happen periodically. As the threats evolve, the previous issues that weren’t considered risks can suddenly become serious vulnerabilities. Patches and improvements should be added regularly.
What should a network security audit include?
Your network security audit should begin by identifying potential threats and vulnerabilities to the organization. This can be achieved by listing all network devices and mapping the network infrastructure. Depending on your business size, this step can take a while.
A typical network security audit will consist of several rounds of reviews of all documented assets’ security status, especially the ones that are reachable from the public internet. This should be followed up with reviews of security mechanisms and practices. Depending on the audit’s focus, it can also be one of the parts of a larger compliance procedure. Audit results provide a list of critical issues and help shape the company’s cybersecurity direction.
Network security audit checklist
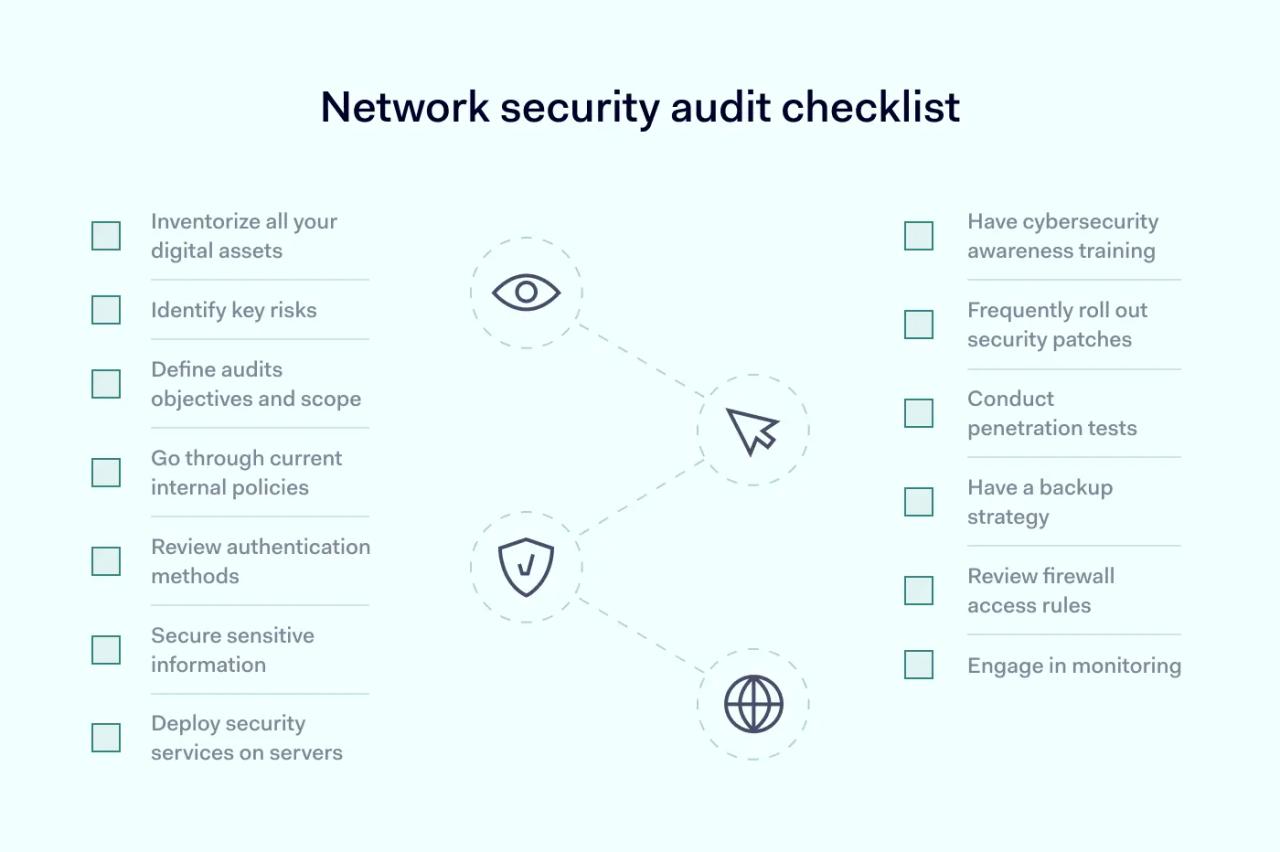
Don’t forget that you don’t have to do everything yourself, especially if you have the resources. However, if you don’t want to rely on third parties and can do it independently, here’s a network security audit checklist that should help you out.
1. Inventorize all your digital assets
Identify all used devices and operating systems on your network. This includes:
- Organization-managed devices
- Unmanaged assets belonging to employees
The list of all these devices will help you to outline the organization’s security perimeter. Don’t forget various unsupervised workarounds on how your employees could access company resources, as they could function as backdoors into your network, i.e., mobile devices.
2. Identify key risks
Make a list of various cybersecurity risks that could be threatening your company. A good choice could be listing the most frequent threats for businesses like malware, insider threats, DDoS, and ransomware. Once you have identified what you’re up against, it will be easier to evaluate security flaws in the right context.
3. Define audits objectives and scope
Your audit needs to have a purpose and scope. This will help you to focus on the task at hand and not stay fixated on the minor details. You should have a good overall view of your current cybersecurity situation, and an audit could serve as a method to identify the areas that need improvement.
4. Go through current internal policies
Revising your company policies can provide invaluable insights into your company’s security. There should be a good justification for how usage, wireless network security, internet access, and other policies are implemented. Better transparency in network security policy areas can have long-term benefits.
5. Review authentication methods
Leaked passwords can be a significant risk, especially if your employees tend to reuse passwords. You should ensure that your employees are using strong and complex passwords and, if possible, implement additional security measures like two-factor authentication. An additional requirement to make password changes mandatory can contribute to overall security.
6. Secure sensitive information
Some assets hold the most sensitive data types, which the hackers target. Therefore, sensitive information should never be stored in an unencrypted form. Never allow unauthorized individuals to access it and restrict employees only to the resources needed for their direct tasks.
7. Deploy security services on servers
Your servers simultaneously provide network connectivity for your organization and host a lot of critical data. Therefore, they should be properly configured to allow only trustworthy connections. In addition, you should have a server list with all used IP names, purposes, operating system versions, etc. In an emergency, you’ll have an easier time getting the service back online.
8. Have cybersecurity awareness training
Nowadays, cybersecurity training should be a part of your onboarding. As employee actions pose a significant risk to your organization’s security, they must be aware of the most common errors. Internal cybersecurity exercises are a good checkup method, checking how many employees opened suspicious links. Invest time and effort to spread the message that cybersecurity is also a responsibility of each employee.
9. Frequently roll out security patches
Always use the latest version of applications, operating systems, and other software. Timely patches are a good way to avoid hackers using newly discovered exploits to penetrate network software systems. It’s also important to keep antivirus applications updated as they retrieve the latest malware databases when detecting malicious files.
10. Conduct penetration tests
Penetration tests put you in a hacker’s perspective and are a good way to discover loopholes that could be hard to find by only focusing on perimeter security. Various tools test applications when they’re not running and active. It’s also a good idea to review whether the currently used penetration testing methods are effective.
11. Have a backup strategy
Backups are one of the business areas that reaffirm age-old knowledge that it’s better to be safe than sorry. Every company should have an emergency plan for data backups, so it’s important to review its process during an audit. A shortcoming in this chain could make your data recovery longer, if not impossible.
12. Review firewall access rules
A firewall is the main gateway for all inbound and outbound connections in your network. Appropriately configuring their rules can be a solid shield against all cybersecurity threats. Close opened but unused ports, and remove permissions from unsupervised connections. Segmenting your internal network is a great tool for better control.
13. Engage in monitoring
Monitoring and analysis of past logs should be key instruments of enterprise security supervision. There should be a company-wide system to collect and review the logs. Always take note of new devices on the network and check their identity and ownership. It’s a good habit to clean up inactive accounts and devices from the system.
Network security audit challenges
No two enterprises will have the same challenges if you’re wondering what potential bottlenecks could be when performing network security audits. For some, the audit scope will be very high, as they’re huge enterprises, so it will be much more time-consuming and expensive. For others, the main problems will be the lack of knowledge to audit or to analyze the audit data.
As with many projects, you’ll need discipline and willingness to achieve better cybersecurity status. Even if you’re on a very limited budget, there are many cost-saving opportunities even when working with a very limited budget. The focus should be on making gradual improvements that would bring value to the organization for years to come.