Companies that work with people's sensitive information must keep that data safe. When it comes to the security of personal data, citizens of the EU are protected by the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
In this article, we'll explore why GDPR security compliance is essential for companies that control and process personal data. Plus, the range of data protection measures that companies can implement to ensure data privacy and security.
GDPR is a set of compliance standards that aim to give EU citizens more control over their personal data. The regulations apply to all companies that work with this sensitive data, even those outside of the EU. GDPR provides a security framework that guides organizations on how to securely process data.
Key takeaways
- GDPR is a set of compliance regulations that aim to protect consumers' data privacy, specifically for citizens or data subjects in the EU.
- The basic information security principles of confidentiality, integrity and availability are important when applying General Data Protection Regulation guidelines.
- Non-compliance with GDPR can result in big fines for organizations, which can be avoided with strong data protection measures.
- Key GDPR security controls businesses can implement include identity and access management, data encryption, incident response planning, SASE and zero trust networks.
- GDPR compliance is not a once-off exercise, but rather a journey. Data security is continually updated to meet evolving threats to ensure personal data is protected, accounted for, and processed correctly.
GDPR's confidentiality, integrity and availability principles
Companies that process data from EU citizens must abide by the GDPR security measures. While GDPR requirements don't prescribe specific tools or processes, companies must use "appropriate technical and organizational measures" to safeguard individuals' personal data. The focus of these data security measures is on "confidentiality, integrity and availability." Basically, ensuring individuals' personal data remains private and secure, is accurate and is accessible to them.

The principles of confidentiality, integrity, and availability — also called the CIA triad — form the foundation of information security. Organizations that implement these elements to create a strong basis for data protection. If data controllers or processors are missing any of the three, it could result in a serious compromise in security.
8 essential security controls for GDPR compliance
Here are eight information and cyber-security measures that can improve your privacy safeguards. Note: companies only need to implement solutions that are appropriate for their business and the risk level of their data processing.
1. Zero-Trust Network Access (ZTNA)
Zero trust network access means that no user is automatically trusted or granted access to a network. Based on the principle 'trust-none, verify all" which forces every user and device to authenticate before gaining network access.
A zero-trust approach supports GDPR by minimizing lateral movement or the attack surface within a network. As a result, a zero-trust approach can minimize the impact of a security breach.

2. Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Identity and Access Management (IAM) policies ensure that every user only has the level of access to data that they need. IAM makes sure that unauthorized users cannot access a company's network.
Within GDPR, these access restrictions means that only authorized users can access the personal data. IAM ensures that anyone handling the personally identifiable information (PII) only has access to what's needed for their specific duties.
3. Encryption and pseudonymization
Data encryption is a fundamental part of cybersecurity. If means converting data into an unreadable format when it's transmitted from one network to another. Encryption supports GDPR compliance by keeping data secure and confidential.
Pseudonymization means removing details from personal data that could be used to identify an individual. In the context of GDPR, that means additional protective measures for PII.
4. Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
A Data loss prevention system prevents the loss of business or customer data through data leaks or the destruction of data. The DLP solution spots any authorized attempts to remove data from the network and alerts the security team.
Some data controllers may choose to use a DLP solution to add extra technical safeguards to prevent the loss of PII, per GDPR. A beneficial idea, considering that both data controllers and data processors can be fined if any personal data is lost.
5. Incident Response Plan (IRP)
If a data breach does occur, companies need a detailed plan, called an Incident response plan (IRP), to handle it quickly and effectively. Per GDPR, companies need to report a data breach within 72 hours. Their IRP plan should include steps such as:
- Preparation for any kind of cyberattack
- Detection and analysis
- Containment eradication and recovery
- Post-incident activities
The reporting structure should start with the data processors reporting any data breaches to the data controller. Followed by the controller reporting to the supervisory body --- the Data Protection Association (DPA). The DPA is the organization that monitors and enforces GDPR compliance.
6. Secure Access Service Edge (SASE)
Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) is another data breach prevention tool that helps companies meet GDPR requirements. SASE is a cybersecurity framework in the cloud made up of networking and security solutions.
One of the main benefits of SASE is that it boosts data, network, and device security with advanced cloud security protocols. The modern framework even covers remote access and SaaS security, all contributing to safeguarding sensitive data.
7. Third-party risk management
Any processor, contractor or subcontractor that processes, stores or transmits the personal data of EU citizens needs to follow GDPR rules. What's more, the controller needs to know exactly how their third-party business partners keep PII secure and minimize risk. Why? Because under the data privacy regulations, everyone that works with that personal data is liable for keeping it safe.
It's a good idea to work closely with third-party vendors to monitor and help improve their GDPR compliance.
8. Policy management
Policies form the foundation of any solid security strategy. Companies with strong policy management practices have an easier time keeping their solutions up-to-date and compliant. Combined with buy-in across the company and workforce education on policies, organizations can work together to better protect their systems and keep cybercriminals out.
The importance of GDPR compliance and data protection
As with any global regulatory compliance, it's important for data controllers and processors to comply with GDPR.
The effects of non-compliance
Non-compliance with GDPR requirements can result in a hefty penalty from the regulatory authorities. Fines can reach up to 4% of a company's annual turnover, with a maximum of €20 million. One of the highest fines to date saw Meta fined €390 million by the Irish Data Protection Commission.
Along with the direct financial loss from penalties, non-compliance can also drive customers away. Data subjects are more likely to put the blame on the company that loses their data than the hackers that caused the data breach. Plus, they may not be quick to forgive organizations that don't put proper data security measures in place, causing a break in trust and brand loyalty.
The benefits of GDPR compliance
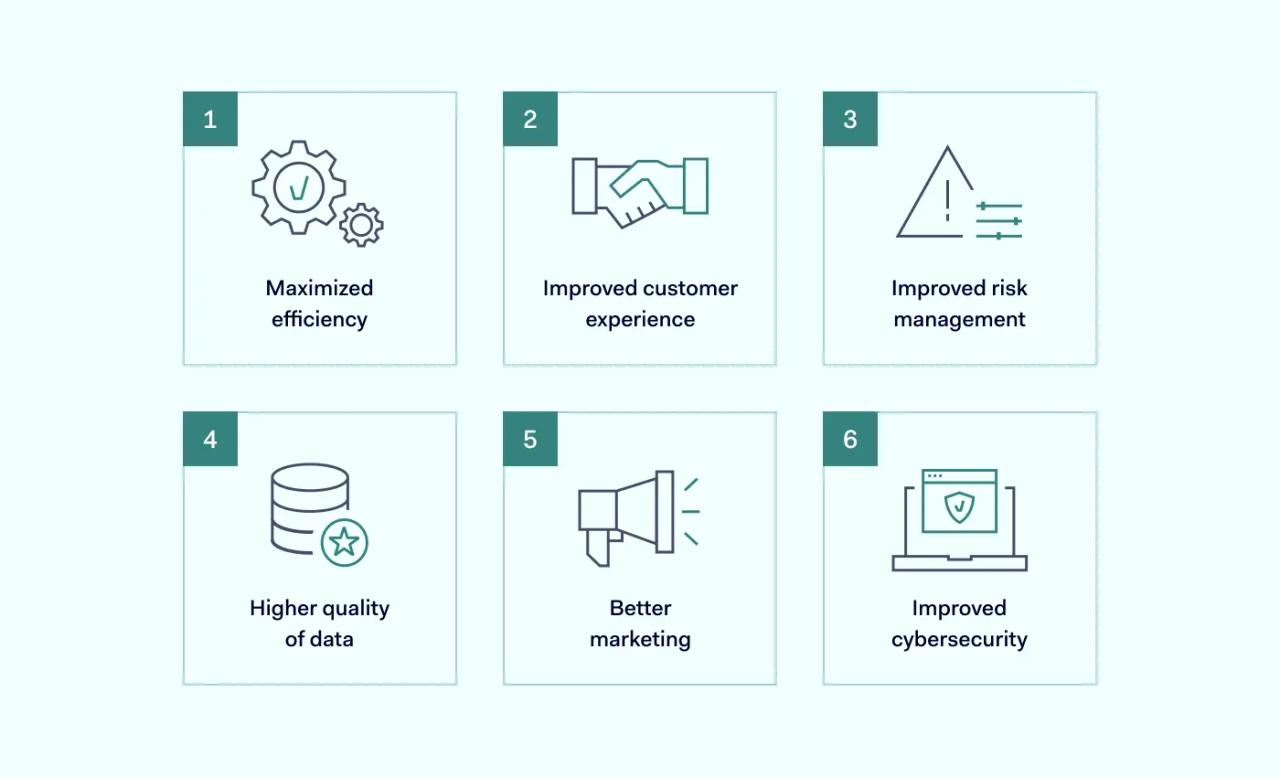
Companies that follow the General Data Protection Regulation framework show their customers that the security of their personal data is a top priority. In the long run, this can build trust with customers, reduce the risk of data breaches and other benefits, such as:
- Using GDPR compliance processes to improve their business processes. For example, streamlining data processing or increased awareness of security vulnerabilities.
- Boosting your brand reputation and credibility. Companies that follow the seven principles of GDPR will get a head start with this.
- Getting better insight into what data the business collects. These insights can help various departments, such as marketing to stick to data privacy rules.
- Improving data management by conducting data audits, for instance.
Implementing GDPR for your business
Ultimately, organizations should remember that GDPR compliance is a journey. It is not a once-off activity, but goes through iterations and improvements as security threats change.
Yet, it is important to implement the right GDPR security controls and compliance measures for your business. This might include a Zero trust approach, data encryption and SASE, or other protection measures that match the level of risk.
By prioritizing data protection and compliance with the General Data Protection Regulation requirements, you're helping to keep data subjects' personal data out of the wrong hands, prevent data breaches, and respect individuals' personal data rights.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and not legal advice. Use it at your own risk and consider consulting a licensed professional for legal matters. Content may not be up-to-date or applicable to your jurisdiction and is subject to change without notice.