Security compliance is the process of meeting established standards and regulations to protect a company's digital assets from cyber threats. By implementing these requirements, organizations reduce the risk of security breaches and any resultant financial losses. Plus, they avoid hefty fines for non-compliance and the high cost of reputational damage.
When a business implements security compliance, it's important for them to understand the difference between similar concepts, such as IT security and compliance, learn from best practices, like continuous network monitoring, and understand the benefits of going beyond compliance regulations to protect their business against cyber threats.
Key takeaways
- Security compliance refers to the rules governing IT security, according to the applicable local or global laws.
- Security is about a company's internal IT rules and processes. Compliance has to do with the industry regulations regarding IT. InfoSec refers to how organizations keep personal or confidential information secure.
- The benefits of security compliance include avoiding fines, preventing security breaches and streamlining data management. The challenges can include handling ever-evolving cybersecurity threats, managing multiple regulations and the increase of remote work environments.
- Security compliance best practices include conducting regular internal security audits, maintaining detailed audit logs and creating a compliance plan.
Security vs compliance: what is the difference?
Security and compliance are terms that are often used interchangeably, which can be confusing. However, they don't mean the same thing. Put simply, security is the processes and tools organizations use to protect their digital assets, while compliance is the rules or standards that govern an organization's information technology. Knowing the difference between similar terminology like compliance, security and InfoSec, can help your business better plan and manage your overall security.
Compliance
Compliance is a collection of regulations, standards and best practices that businesses must adhere to. The requirements can align with local or global laws and, in the IT industry, are all about data privacy and security.
The core compliance protocols focus on the protection of sensitive data, typically relating to health records , financial transactions and other personal information. Examples of these important compliance criteria include the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS) and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA).
Companies usually have a specific team that is responsible for monitoring and implementing compliance. By meeting the requirements of your industry and region, the compliance team helps to reduce the risk of cyberattacks. However, focusing on compliance alone does not guarantee that your business and customer data will be safe and secure.
Security
Security or IT security refers to the strategy and tools that protect a company's digital assets from unauthorized access. The IT security team protects the organization's computers, networks and data from malicious attacks through methods, such as access management and cloud security.
An up-to-date IT security strategy minimizes vulnerability to attacks and data breaches, making it essential for any modern business.
While IT compliance and security both aim to improve the security of your organization's digital assets, there are a few fundamental differences between the two.
Security:
- The systems and tools that protect a company's digital assets
- Prevents cyberattacks, data breaches and other unauthorized access
- Internally motivated by the business
- Managed by the IT security team
Compliance:
- The rules and regulations about cybersecurity
- Facilitates industry best practices and reduces risk of penalties
- Required by third parties like the government or industry bodies
- Managed by a compliance team
Interestingly, even with these differences, security and compliance fit together or complement each other. This is because compliance alone does not guarantee good security. By aligning security and compliance measures, and having both these teams work closely together, businesses have the right level of control to boost security and ensure compliance.
InfoSec
Another term that is sometimes confused with compliance and security is information security (InfoSec). InfoSec is about keeping an organization's personal or confidential information safe through components, such as application security, cloud security, and disaster recovery.
Focusing specifically on data privacy and data protection , InfoSec ensures that all your business information is protected from attacks like third-party breaches, whether the data is being transferred, processed or stored. At the same time, information security grants employees access to the information they need while preventing unauthorized access.
All three of these components — compliance, security and InfoSec — form part of an organization's security strategy, and work together to block cybersecurity threats.
The importance of security compliance in protecting your business
Implementing compliance frameworks is not enough to protect your business's digital assets. Organizations need to go beyond compliance and implement strong security measures to ensure their data is secure, and, as a result, build trust internally and externally.
Benefits of implementing security compliance
There are many rewards for your business when you implement security compliance measures.
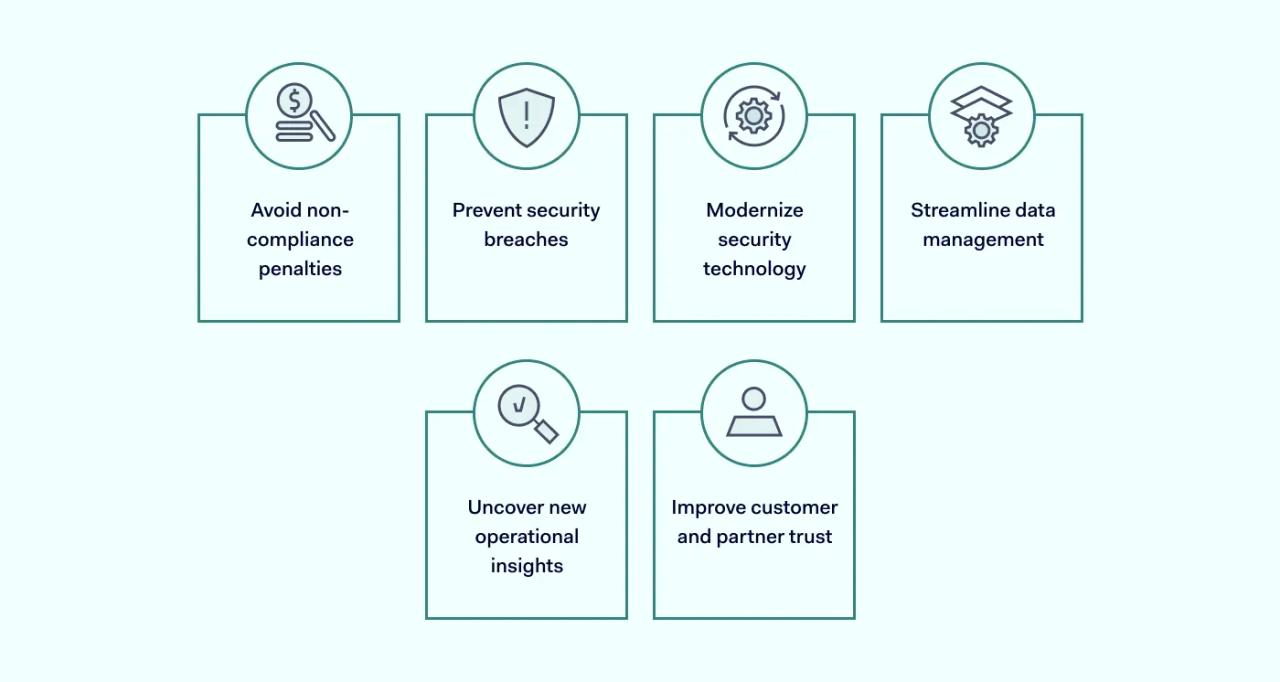
Avoid non-compliance penalties
It's natural that companies would want to avoid fines or financial penalties for non-compliance, especially since fines can be as much as €20 million or 4% of a company's annual global turnover for major EU GDPR violations, for instance. There's also a risk that non-compliance can result in a data breach, causing major financial losses and dire reputational damage.
Prevent security breaches
When a company implements best practices with their IT security, such as a Zero Trust approach, and aligns with the relevant regulatory compliance, such as the HIPAA Act, they create a strong security strategy that reduces the risk of a data breach and keeps their data safe.
Modernize security technology
In the process of ensuring compliance, many businesses also upgrade their security tools, such as adopting an enterprise-wide Virtual Private Network (VPN). Other examples of advanced security tools include firewalls, Identity and Access Management (IAM) software and data encryption tools.
Streamline data management
When businesses implement security compliance measures, they often need to update their data management practices too. Data management refers to how a company receives, stores and maintains data. With structured data management practices, organizations can streamline their processes and improve efficiency.
Uncover new operational insights
During their compliance journey, organizations may uncover helpful insights into workflows that could, for instance, improve the security of customer interactions. For example, a healthcare provider may realize that an upgrade to their health app has introduced data encryption concerns that they need to resolve so their customers' data remains secure.
Improve customer and partner trust
Your customers and other stakeholders want to know their data is safe in your hands. Being compliant demonstrates that you prioritize the safety of their personal or sensitive information, such as their social security number or personal health details.
3 main industries affected by security compliance
Many industries deal with critical or sensitive information and have rules or standards they must apply to keep the data secure. Three industries that are highly impacted by security compliance include healthcare, financial services and government.
1. Healthcare
Healthcare security compliance includes regulations such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). This set of rules ensures any company that deals with healthcare data keeps that data secure at all times. It also covers aspects such as the confidentiality, availability and integrity of this protected health information or PHI.
2. Financial services
Financial services providers are responsible for people's funds. Keeping financial transactions secure, especially digital banking, means keeping ahead of financial fraud schemes, which change every day. That's why regulations such as Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), Payment Service Directive, revised (PSD2) and GDPR play a key role in protecting consumers from fraudsters.
3. Government
Along with regulations such as the EU Cybersecurity Act and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), federal agencies must also comply with Federal Information Security Management Act (FISMA) and the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Cybersecurity Framework to keep the citizenry's data secure.
A few common challenges in achieving cybersecurity compliance

For some organizations, the compliance journey is not easy. Being aware of a few common challenges can help teams plan for success.
- Continually evolving security threats — cyber threats are constantly changing and becoming more sophisticated as cybercriminals take advantage of technological advances.
- Managing multiple regulations — compliance needs to cover your industry requirements but also any rules about operating in different countries.
- The expansion of remote working models — as companies enable new ways of working like remote and hybrid working models, the complexity of their security compliance grows too.
- Maintaining infrastructure for growing teams — dealing with larger teams inevitably requires more infrastructure coordination and compliance management.
- Relying on legacy technology — since cybercriminals leverage the latest technology and innovations, outdated technology poses a big security risk and may fall short of the latest cybersecurity standards.
Along with being aware of common security compliance challenges, teams can make steady progress in their journey by incorporating best practices into their approach.
9 best practices for improving your security compliance
Help your business get extra traction with your regulatory compliance by considering these practical industry best practices.
1. Conduct internal security audits
The information security team can conduct an internal audit of the company's cybersecurity infrastructure to determine how effective the current security approach is. This voluntary review or risk assessment can make external audit processes smoother and less stressful.
Plus, internal audits can help the team identify and prevent threats that could occur after installing a company-wide software update or introducing a new third-party app, for instance.
2. Use audit logs
Another way your business can streamline external audits is by using audit logs. These are records of all software system activity in the organization, such as system accesses and operations that users have performed. Audit logs provide the evidence you need to prove compliance with your relevant standards or industry rules.
3. Monitor your network 24/7
Teams that utilize software to continually monitor network activity can quickly detect and respond to any anomalies and prevent security risks with efficient incident response.
By conducting internal audits and 24/7 network monitoring, it becomes easier for security teams to prevent cyberattacks, rather than be reactive and scramble to reduce the negative impact of a breach.
4. Create a compliance plan
While compliance is a set of specific rules or frameworks, it's up to companies how to implement compliance standards across their organization. A comprehensive compliance plan should get all stakeholders, including IT, compliance, HR and certain execs, on the same page when it comes to implementing and maintaining all compliance components.
5. Adopt a zero-trust approach
A zero-trust approach to security means that the security protocols are extremely strict, and assume that no network traffic is trustworthy. This method effectively controls network access through measures like 2FA, biometrics and SSO, and provides better security than perimeter-type solutions, like firewalls.
6. Encrypt data transfers from untrusted networks
In industries, like healthcare, data privacy and data security is vital. Organizations that encrypt data transferred from untrusted networks , for instance, help to prevent any unauthorized access and keep the data safe.
7. Develop a strong risk management plan
In addition to a compliance plan, creating a risk management plan can help your organization prepare for potential cyberattacks. The plan will uncover any existing security vulnerabilities or risks, like ramping up remote access and help your business manage and minimize any potential impact.
8. Implement strategic access management
Limiting or segmenting access based on specific requirements or duties will protect your company's digital resources and reduce the movement of cybercriminals if there is a breach. For instance, only the information security team should have access to your VPN software.
9. Keep all computer software up to date
When software is not up to date, it becomes more vulnerable to attack. With new threats evolving all the time, your business needs the latest updated software to remain secure. For instance, keeping software patches up to date is always a priority for IT security teams.
Align your security and compliance for maximum network protection
NordLayer provides advanced tools that help organizations effectively align security and compliance. By integrating our automated solutions into your compliance strategies, you can easily meet your compliance requirements and keep your digital assets secure.
