Thinking about ISO 27002 certification for your organization? This guide will help you decide.
What is ISO 27002?
ISO 27002 is a leading global standard for implementing controls for information security systems. Intended to supplement the ISO 27001 framework, ISO 27002 is an essential resource for companies dealing with the information security aspects of compliance and privacy protection. This article explores the content of the 27002 standard and how organizations can use it to boost their information security posture.
Key takeaways
- ISO 27002 is a register of information security controls that supplements ISO 27001. The 27002 standard guides organizations about meeting ISO 27001 requirements. It is an essential tool when building a compliant information security management system.
- ISO 27002 enhances security awareness and helps select appropriate controls to mitigate risks. It also makes achieving ISO 27001 certification easier, gives companies greater control over information assets, and boosts trust among customers and partners.
- The 27002 framework includes 93 controls grouped into four domains. Control areas include cryptography, threat intelligence, human resource security, physical security, access control, secure coding, business continuity, and securing cloud services.
- Core requirements of 27002 include documenting and assessing information security risks. Companies should research Annex A controls before implementation, execute gap analysis, and align controls with the organizational context.
What is the purpose of ISO 27002?
ISO 27002 is part of the library of information security standards maintained by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC).
The ISO/IEC created ISO 27002 to fill a gap in its information security library.
Annex A of ISO 27001 lists security controls and policies. However, it does not provide detailed information about how to implement those controls. ISO 27002 provides this information.It guides organizations in creating an information security management system and supplements ISO 27001, providing advice about suitable security techniques and controls.
ISO 27002 offers a range of best practices for ISO 27001 Annex A domains. It provides an international standard for areas like physical security, access management, human resources management, and how to structure an information security management system.
Organizations can use ISO 27002 to create information security controls that lock down confidential data and prevent data breach attacks. Combined with ISO 27001, the 27002 information security standard makes it easier to apply risk-based controls across all information assets.
Benefits of ISO 27002
Organizations do not have to refer to ISO 27002 when creating an ISMS. However, the framework contains many relevant practices and recommendations. Other benefits of consulting ISO 27002 recommendations include:
- Improved security awareness. Organizations can use ISO 27002 to assess their options and find controls to mitigate critical risks. Without using ISO guidance, companies can miss valuable security techniques.
- Smoother ISO 27001 certification. ISO 27001 certification requires the implementation of relevant and effective controls. ISO 27002 documents potential options and cuts the risk of a failed external audit.
- Continuous compliance. ISO regulations require constant monitoring to check compliance and apply corrective actions. ISO 27002 helps you implement auditing and logging systems. Continuously managing risk enables you to source corrective controls when needed.
- Better asset control. Organizations implementing ISO 27002 recommendations have more control over asset storage and use and information deletion. Compliance boosts awareness of sensitive information assets. Robust information security controls also prevent unauthorized access.
- Customer and stakeholder trust. Companies implementing ISO 27002 controls can use their ISMS to show they are committed to security and privacy protection. Compliance boosts trust and smooths client or supplier relationships.
- Cutting-edge security. ISO 27002 information security controls are regularly updated to reflect state-of-the-art technology. For example, the ISO 27002:2022 standard includes valuable advice about secure cloud services, network security, and threat intelligence.
- Streamlined compliance. Regulations like GDPR and HIPAA require a robust information security management system. ISO 27002 includes privacy protection techniques like data masking, network access controls, and physical controls. Companies can pick whatever information security controls they need to achieve regulatory compliance.
- Efficiency and reduced costs. Companies that focus on data leakage prevention suffer fewer security incidents. ISO 27002-compliant companies incur lower costs to fix problems and compensate users. They also find it easier to retain security-conscious customers.
ISO 27002 controls list
The updated ISO 27002:2022 framework includes 104 information security controls. The updated control list covers the following general areas:
Access control
According to Section 5.15, organizations should apply logical access rights to all information assets. ISO IEC 27002:2022 allows organizations to select an access management system that suits their needs. However, access should always be limited to individuals with a business need.
Threat intelligence
Section 5.7 of ISO 27002 requires organizations to collect, analyze, and understand threat intelligence. This process seeks to understand critical threats, classify risks to information assets, and implement suitable mitigation actions.
According to ISO 27002, threat intelligence must be:
- Relevant. Organizations should focus only on real-world threats to their core assets.
- Perceptive. Intelligence must take account of all possible attack vectors.
- Contextual. Analysts must understand how threats affect information security.
- Actionable. Intelligence should lead to mitigation actions and enhanced defenses.
Security teams should take a strategic view of the general threat environment. They should gather operational data about attack methods. And they need tactical information about current threats.
Information security and the use of cloud services
The 2022 iteration of ISO 27002 includes extensive guidance regarding securing cloud-hosted information assets.
Section 5.23 of the framework advises organizations about acquiring, using, and exiting cloud services. This section takes a risk-based approach to using cloud services. It focuses on ensuring data availability, integrity, and confidentiality.
According to the ISO, applying section 5.23 is a collaborative task. Cloud users must cooperate with suppliers to secure information in the cloud. Relevant security issues include:
- Choosing cloud providers
- Roles and responsibilities of cloud vendors and clients
- Using security services provided by cloud platforms
- Secure supplier relationships with cloud providers
- Secure change management in the cloud
- Managing security incidents relating to the cloud
- How cloud services fit into the information security management system
ICT readiness for business continuity
Section 5.30 of ISO 27002 deals with ensuring ICT continuity during adverse events. The core purpose of this section is to protect data integrity and confidentiality during security incidents.
ISO 27002 recommends that companies complete a Business Impact Analysis (BIA) before implementing Section 5.30 controls. Controls should align with business guidelines and goals, including recovery time objectives (RTOs).
RTOs should consider different events. For example, the RTO for enterprise-wide disruption may be longer than outages at a single data center. Continuity plans should also reflect risk assessment information, allocating more recovery time when attacks compromise sensitive data.
Continuity plans require regular testing. There should be a leadership plan to guide recovery. And plans should include key metrics like recovery point objectives for critical assets.
Monitoring physical security
ISO 27002 control 7.4 deals with security requirements for physical locations. Physical security includes managing physical access systems and ensuring only authorized individuals can access confidential data stores.
Organizations should implement controls that detect unauthorized intruders. Intruders include outsiders as well as employees lacking proper clearance. Physical security monitoring should address core risks, including:
- Theft of employee devices
- Use of insecure external devices leading to malware infection
- Data exposure due to improper access control
- Loss of data through negligence
Recommended controls depend on the security environment. They may include surveillance cameras, alarms, and physical guards. Controls also cover control systems like locks or card scanners.
Configuration management
Section 8.9 of the ISO 27002 controls list deals with configuring systems securely. Companies must implement secure configurations for software or hardware dealing with confidential data.
Configuration management involves changing default passwords and following vendor guidance about best practices assets. Ensuring every asset has a security owner is also critically important.
Each asset should have a configuration policy that defines a secure configuration. Policy components include defining access policies, managing identities, and controlling access to third-party software. Logging systems should also detect security problems.
Information deletion
Section 8.10 requires asset management practices that delete information securely. There should be no way for unauthorized individuals to recover data once its business case or regulatory status has expired.
ISO 27002 advises organizations to delete data when no longer required to avoid undesirable disclosure. Companies should log deletions. They should request verification of deletion if they use third-party vendors.
There are also specific deletion guidelines for information systems. For instance, deletion should extend to temporary files or legacy versions of apps. Degaussing should erase magnetic media. Companies may also nee to physically destroy external media devices.
Data masking
Section 8.11 advises organizations about how to mask data to ensure a suitable level of anonymity. Data masking applies particularly to sectors that handle personally identifiable information (healthcare or finance are good examples).
ISO 27002 advises about how to choose between pseudonymization and complete anonymization. It includes recommendations about segregating masked data from other information. And it covers processes to share masked data with third parties.
Data leakage prevention
Data leakage prevention is a core task for any information security management system. Section 8.12 of ISO 27002 includes comprehensive recommendations about preventing breaches, limiting exposure, and securing data.
This control advises about classifying data and securing data channels. It includes guidance about controls like permissions management and access control measures. And it covers data leadership measures, such as requiring management approval for mass data transfers.
Section 8.12 also includes recommended tools to log data and detect breaches. It advises companies to use systems that track data risks and alert security teams about unsafe user behavior.
Monitoring activities
Section 8.16 deals with monitoring network assets to prevent security incidents. According to ISO 27001, companies should monitor activity proactively and continuously. ISO 27002 documents strategies for achieving this.
Monitoring should focus on compliance needs and the risk assessment process. Elements include audit systems, vulnerability scanning, risk evaluation, and real-time user monitoring. Organizations should implement inbound and outbound data tracking. Tracking tools should monitor access to business applications or servers and integrate event logs from vendors as needed.
ISO 27002 advises using behavioral analysis to compare user activity against a normal baseline, providing alerts when systems detect suspicious behavior.
Web filtering
ISO 27002 control 8.23 advises companies about filtering access to dangerous internet destinations. Web filters can prevent employee access to potential sources of malware. And they can also cut the risk of phishing attacks.
Security techniques in this section include IP address blocking and restricting sites with information upload features. Companies should use intelligence to defeat known threats and limit content based on text or image data. ISO 27002 also connects this section to staff training guidelines in ISO 27001.
Secure coding
Section 8.28 of ISO 27002 aims to prevent security incidents arising from poorly coded web-facing assets. Specific areas of concern include weak input validation or key generation systems.
Companies should extend secure coding principles across all departments and software assets, including those supplied by third parties. Security teams should be aware of the latest coding-related security threats. And where applicable, they should use integrated development environments to secure coding operations.
ISO 27001 vs ISO 27002. What are the differences?
Most organizations crafting information security controls encounter both ISO 27001 and 27002. This is a good thing, as the 27002 framework supports ISO 27001 and makes it easier to design compliant information environments. This table should clear things up by showing how the standards differ:
ISO 27001
- The central ISO standard for information security management
- Sets out core requirements of an ISMS
- Includes details about policies, procedures, and controls
- Focuses on identifying and managing risks
- Use when planning an ISMS implementation
ISO 27002
- Supplementary standard that supports ISO 27001
- Provides concrete guidance about how to meet the core requirements of an ISMS
- Focuses on applying security controls. Relatively little emphasis on policies.
- Provides tools to mitigate risks
- Use when implementing an ISMS plan
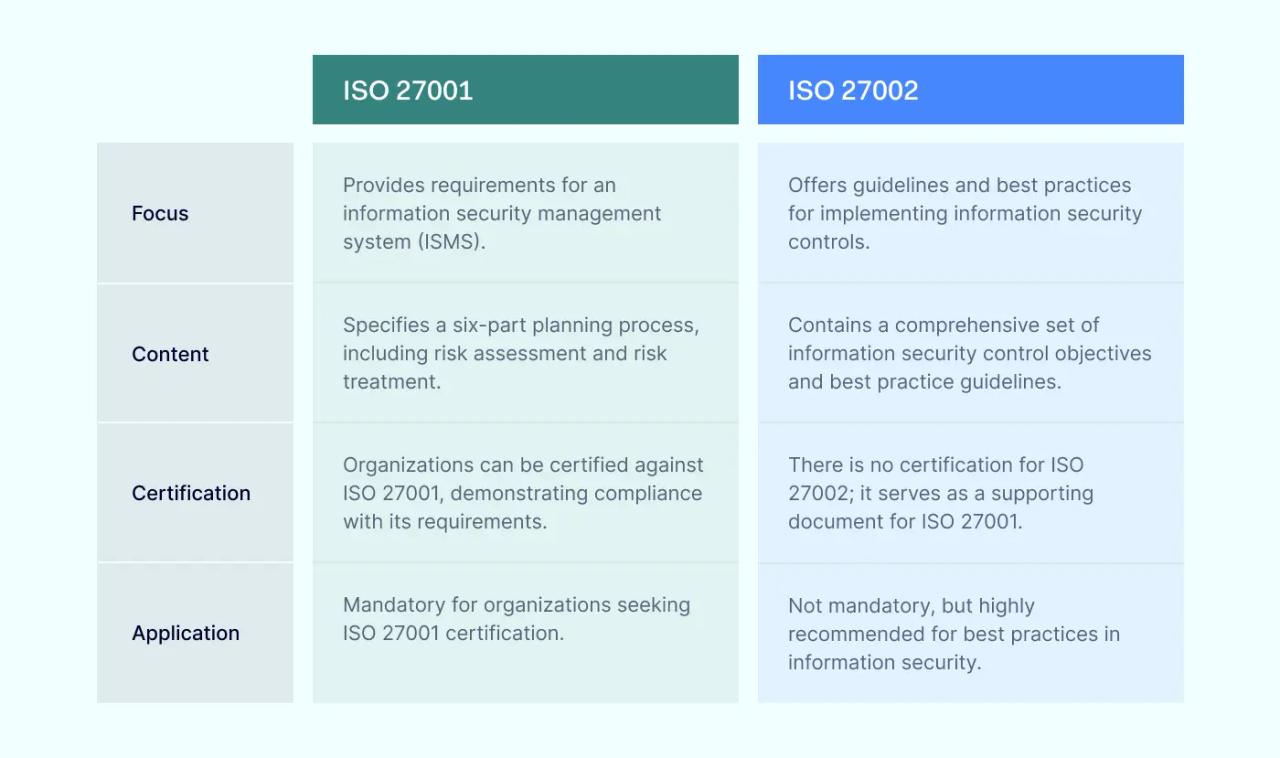
Generally, you should use ISO 27001 to plan and design an information security management system. The 27001 standard provides a comprehensive framework to assess risks, inventory assets, and plan policies and controls.
ISO 27002 puts ISO 27001 into practice. It advises about mitigating risks and reinforcing security policies with controls. Combining the two documents is a best practice when optimizing information security processes.
ISO/IEC 27002:2022 vs ISO/IEC 27002:2013. What has changed?
ISO standards constantly change, and ISO 27002 is no exception. For a decade, the dominant iteration was ISO 27002:2013. However, ISO 27002:2013 is now out of date. ISO 27002:2022 is the best version for companies to consult.

The transition from 27002:2013 to 27002:2022 brought some significant changes. The most far-reaching change reduced the number of controls from 114 to 93.
The 2013 framework grouped Annex A controls into 14 domains. These domains encompassed critical security areas such as access controls, human resource security, cryptography, asset management, and physical and environmental security.
The 2022 framework takes a different approach. Annex A now has four domains. These are people, organizational, technological, and physical controls.
ISO 27002:2022 also added new controls in the areas listed above. For example, the document now provides extended guidance on using threat intelligence, ensuring business continuity, and implementing secure coding.
Recent changes to the 27002 standard reflect the shifting threat environment and new compliance regulations. The standard will undoubtedly evolve in the future, but at the moment, it provides state-of-the-art advice about achieving an ISO 27001-compliant ISMS.

Requirements for ISO 27002
The requirements defined by ISO/IEC 27002 tend to expand sections of ISO 27001. Compliant organizations have to meet a similar set of obligations. Requirements include:
- Documentation for ISO/IEC 27002:2022. Documentation must define the ISMS scope and information security policy. Documentation includes risk assessments, a risk assessment report, and a risk treatment plan. A Statement of Applicability is also essential.
- Gap analysis. Companies must compare their existing ISMS with ISO 27002 requirements. An external gap analysis shows areas of improvement and allows the organization to create an implementation plan.
- Risk management. Organizations must carry out a risk assessment for controls implemented as part of an ISO/IEC 27002 plan. Each control must mitigate a specific information security risk and be proportionate to the level of that risk.
- Meeting the CIA triad. An ISO/IEC 27002-compliant ISMS should balance confidentiality, integrity, and availability. Security teams should use the CIA triad to guide decisions about policies and technical controls.
- Continuous compliance. Security controls should function continuously, protecting data and adapting to emerging threats. Organizations must regularly audit their ISMS and proactively seek areas of improvement.
How to achieve ISO 27002 compliance
Complying with ISO 27001 and ISO 27002 is demanding but manageable. Successful compliance requires a systematic approach based on risk assessment. Companies must also allocate sufficient resources to source new technology or change existing security processes.
Before starting an ISMS design, compliance teams should fully understand the ISO 27002 standard. They should learn the many recommended controls and compare the control list to their security management setup. Instead of relying on third-party guidance, it makes sense to source the ISO 27002 standard, which you can order here.
Keep in mind that ISO/IEC 27002 is a supplement to ISO 27001. Use 27002 as a tool to meet 27001 requirements, not as a guide in its own right. Only implement controls that suit your organizational context. If necessary, bring in external expertise. Consultants can prevent over-regulation and advise about critical controls.
Conclusion: Use ISO/IEC 27002 to ensure ISO 27001 compliance
ISO 27002 is an essential supplement to ISO/IEC 27001. The 27002 standard provides invaluable guidance about appropriate security controls to meet ISO 27001 requirements. It is also a comprehensive tool, supplying advice for virtually all economic sectors. Order the standard today and design an ISMS to mitigate information security risks and neutralize critical threats.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and not legal advice. Use it at your own risk and consider consulting a licensed professional for legal matters. Content may not be up-to-date or applicable to your jurisdiction and is subject to change without notice.
