Business data protection is a necessity and a challenge for business IT administrators. To be the most effective, it needs thorough planning and strategic vision. It outlines how your network will be protected from various online threats.
However, it's not the only thing that this plan should include. It should also cover guidance for your users on the appropriate cyber behavior. The plan should also align with your business model and be a digestible document for easier adaptability and transition.
To make your planning easier, we'll provide some guidelines on what you need to make your network security implementation smoother. This will help you learn the ropes when starting your network security plan.
Key takeaways
- A network security plan organizes IT infrastructure to prevent unauthorized access. It requires regular updates for compliance.
- Network security protects data, prevents cyber attacks, ensures business continuity, and builds trust.
- Implementing network security starts with cataloging assets and identifying risks. These steps shape the strategy.
- Developing the plan includes securing assets within a budget and training staff effectively.
- Executing the plan involves following a timeline, monitoring, and adjusting to new risks.
What is a network security plan?
A network security plan is a strategy to organize your company's IT infrastructure to prevent unauthorized access and other accidents that could compromise its data integrity. The plan details procedures to ensure security requirements are met and establishes actionable security policies.
It's important to note that the plan should evolve: it requires regular reviews to ensure it aligns with regulatory compliance. Various regulatory requirements are also subject to change, which means the document should be revised to reflect these requirements.
On the organization's level, the maintenance of this document falls on the information security officer or a chief compliance officer. Regardless of who manages this side of things in your organization, it should be the person who can effectively communicate the policy requirements so that the document would be executed practically.
Why is network security important?
Network security is vital for organizations as it protects sensitive data from unauthorized access. This protection ensures the confidentiality and integrity of valuable information. It defends against various cyber threats, which maintains business stability and efficiency.
Network security also fosters customer trust and aids in meeting regulatory requirements, reducing legal and financial risks.
A network security plan is beneficial for organizations in several ways:
- Data protection. It keeps confidential information safe from unauthorized access.
- Cyber attack prevention. This plan guards against threats like malware and hacking.
- Business stability. It ensures the smooth running of operations, reducing downtime.
- Legal compliance. The plan helps in following data protection laws and standards.
- Customer trust. It shows a commitment to protecting client data.
- Reduced costs. The plan lessens the expenses linked to data breaches and their impacts.
- Network performance. It helps in managing network traffic effectively, improving efficiency.
How is network security implemented?
To begin network security implementation actions on your end, it's useful to look at the matter overall.
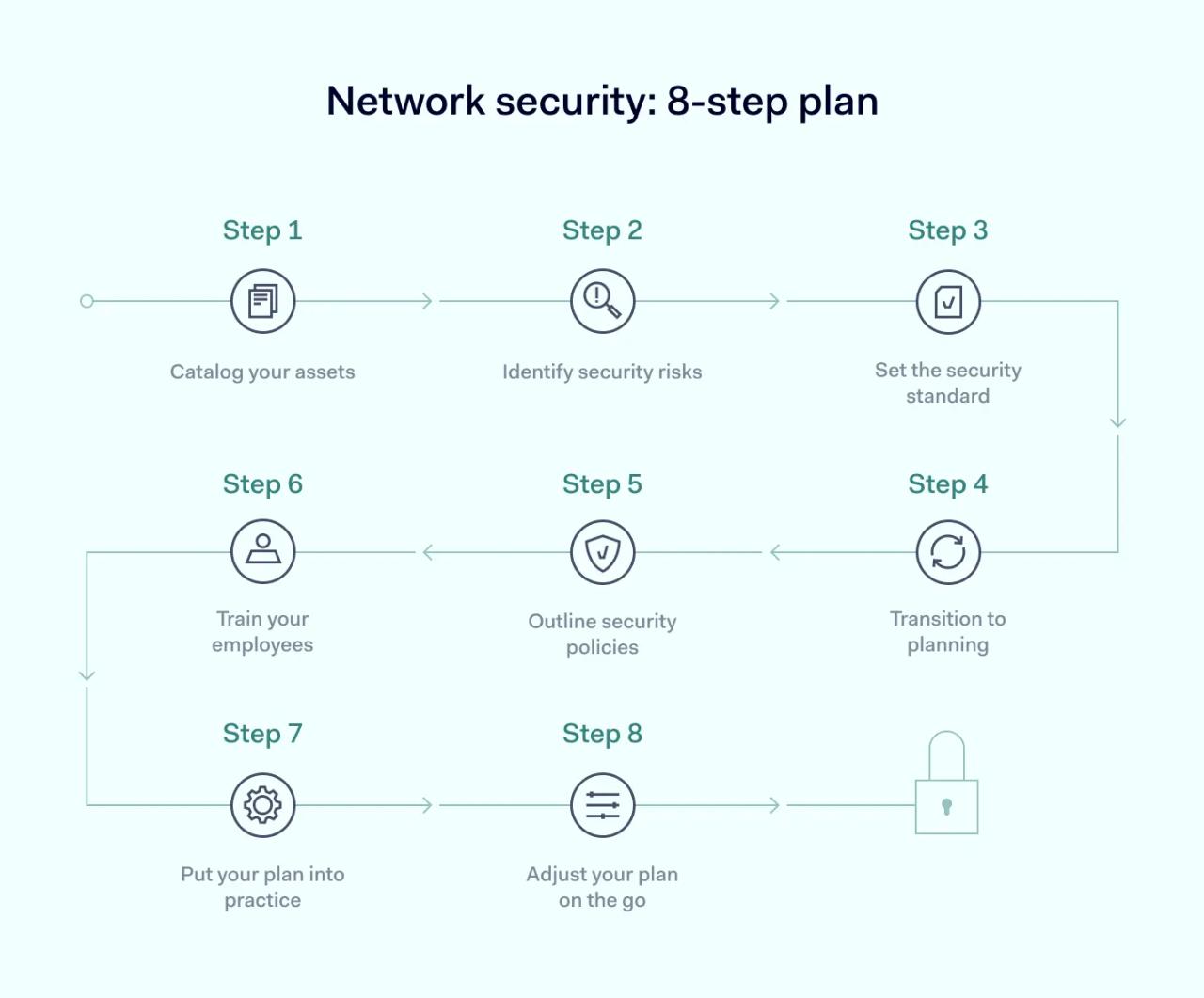
Here's an example of how a security professional could approach security model adaptation in a company.
1. Catalog your assets
The first step should be to catalog all the organization's assets connected to the internet. It will shed light on the scope of the protection that needs to be introduced and will help to shape your network security strategy.
The list should include all devices ranging from servers to employees' laptops — anything that stores business data. The devices that store the most sensitive data types should be best secured. However, don't forget to check which devices pass data over what networks. This may reveal weak spots in your infrastructure.
2. Identify security risks
Each asset that you've identified is susceptible to various security risks. However, some risks are very severe and require immediate solutions, while others may be more hypothetical. The key to this part is identifying the most likely and the most dangerous risks.
An example of such a risk could be a data breach due to unencrypted communication channels or an insider threat that could leak company data externally. Remember that risk assessment shouldn't be done once and forgotten — it should be a routine process as your business develops.
3. Set the security standard
Once you know what assets you're using and what risks are the most likely, it's time to evaluate what security requirements you should set up. Some budgeting options should also come into play as, depending on the area, it may prove easier or harder to secure, which can affect its final price tag.
You may also run into some limitations like legacy hardware, which means that in some cases, the only possibility to avoid risks would be to replace some legacy systems altogether. However, as a rule of thumb, try to set a total budget and plan to fit it.
4. Transition to planning
If you've completed the first three steps, you have all you need to develop your security plan. The assets have to be secured in such a way as to eliminate identified risks using various methods within a set budget.
The plan should detail how various assets will be secured and how the new solutions or approaches directly help address found network flaws. This part should also transition into an implementation strategy that could be converted into tasks that the technical employees should implement.
5. Outline security policies
Up to this point, your network security plan focused on the technical parts. What you shouldn't forget is that you should raise security standards for your employees, as well as your assets. At the most rudimentary level, it should include various guidelines each employee should follow when accessing work resources.
Outline the acceptable and unacceptable use cases of network assets. In addition, detail how various access permissions will be assigned. This will help ensure that the employees aren't exposed to the full network data set, which helps to ensure its security.
6. Train your employees
Regarding employees, it's not enough to set rules and expect everyone to know how to apply them in practice. Even if your employee network security guidelines are basic, you should still conduct company-wide training. Conducting compliance training to ensure employees understand what's at stake and what's expected of them is not a bad idea.
Your IT personnel will also require training, which should be more in-depth. As they will be directly ensuring the maintenance of the system, IT staff should be qualified to use and resolve any errors that will arise from the new systems.
7. Put your plan into practice
Finally, the strategy you've come up with should be implemented. To have a smooth transition, you should put your plan in a timeline — note all outsourcing requirements you'll need and identify which improvements will require how many person-hours.
This is also a good step to evaluate how many contingencies you could expect. This should be reflected in your plan, as the more tricky improvements should have some room for time. This will help to move forward with the implementation actions and not get delayed far behind.
8. Adjust your plan on the go
The last note should be that your network security plan's work doesn't end with its implementation. You should continuously monitor and evaluate its performance to see what could be improved or altered. As the risk landscape changes, this should shape your network security plan. However, the adjustments should be made the same way the plan was implemented.