Finding a company that doesn't use computers or the internet would be hard. Naturally, cyber-attacks are a risk to almost all modern businesses. Therefore, a security plan must be in place, especially in the current climate when online attacks are on the rise.
A network security audit gives a good insight into a company's security posture and overall security controls. Timely audit process can indicate huge cybersecurity risks that, when patched, could improve an organization's security state. In this article, we'll present everything you should know about creating a network security audit checklist to help you improve your cybersecurity.
Key takeaways
- Almost every company uses computers and the internet, making them targets for cyber-attacks. A security plan and proper access controls are crucial.
- A network security audit provides valuable insights, helping to identify and patch significant cybersecurity risks.
- An audit checklist organizes the complex audit process, ensuring all critical areas are covered.
- It helps detect vulnerabilities and ensures compliance with regulations, reducing legal risks.
- It improves incident response and recovery by identifying potential failures.
- Regular updates, patches, and awareness training help prevent breaches before they occur.
- Audits guide where to invest in security, ensuring money is spent on necessary improvements.
What is a network security audit?
A network security audit evaluates all of the company's network systems to eliminate potential security risks. It involves a detailed audit process that reviews access and security controls, and policies to determine the company's current status security-wise. This process also helps strengthen incident response readiness and improve threat detection capabilities across systems.
Devices like servers, laptops, smartphones, and even virtual gateways should all be screened to ensure they're safe to use. Generally, five different key areas must be checked:
- Control implementation-Based on the importance of the assets, various security controls have to be implemented to limit data exposure and restrict access controls
- Management practices-Bad habits in cybersecurity management can severely backfire, so it's essential to ensure that the processes use the best practices
- Network availability-All applications and data must be available for users immediately when needed
- Network security-Computer networks with access to the internet serve as attack surfaces, so their security is central to the overall network security posture
- Overall performance-The general performance of an organization's IT systems is a significant factor that, when resolved, could improve work performance
Investigations of these areas and resolving found issues can drastically improve an organization's security posture and overall efficiency.
Why do you need a network security audit checklist?
Current computer network systems can be so complex that the list of areas that must be supervised is quite extensive. Due to its scope, a network security audit checklist helps to make the audit easier by putting it in a systematic approach. It's the easiest way to ensure that everything that should be secured is checked for issues.
When should a network audit be performed?
A network audit can verify your network's readiness for any task. Be it a network migration, rolling out a new service, or routine maintenance.
You can consider network assessment in various scenarios:
- Preparing for network migration: an assessment pinpoints potential compatibility challenges before transitioning your network to fresh infrastructure, ensuring a smooth transition.
- Launching new services: before introducing services like cloud apps or a VoIP system, an assessment verifies your network's capability and set up to support these additions.
- Scheduled upkeep: regular assessments keep your network running optimally, catching issues before they escalate.
- Following significant updates: post major updates, whether hardware, software, or configuration alterations, an assessment confirms everything functions correctly and maintains integrity of security controls.
- Meeting regulatory demands: specific sectors and entities must comply with standards such as HIPAA, PCI DSS, or GDPR, necessitating regular assessments for compliance.
- Addressing security alarms: should there be concerns over a possible compromise or a past security incident, an assessment can uncover vulnerabilities or security loopholes that might have played a role.
In short, routine network audits, especially before significant changes or service introductions, are key for maintaining an efficient and secure network, allowing you to resolve potential issues proactively and strengthen incident response measures
How to conduct a network security audit?
To conduct a network security audit effectively, follow these steps:
- Define the audit scope and objectives. Identify which systems, devices, and data are in scope. This ensures a clear and focused audit process.
- Review current security and access controls. Document what protections are in place and assess their effectiveness in safeguarding data.
- Assess vulnerabilities through threat detection tools. Analyze logs, configurations, and network traffic for suspicious behavior or weak points.
- Evaluate the company's security posture. Compare current measures against best practices and compliance standards to identify improvement areas.
- Test incident response procedures. Conduct tabletop exercises or simulations to see how well the team reacts to potential breaches.
- Generate and review the audit report. Summarize findings, highlight risks, and recommend improvements to threat detection systems.
A well-conducted audit process strengthens your organization's cybersecurity and ensures continuous improvement in its management.
Network security audit checklist
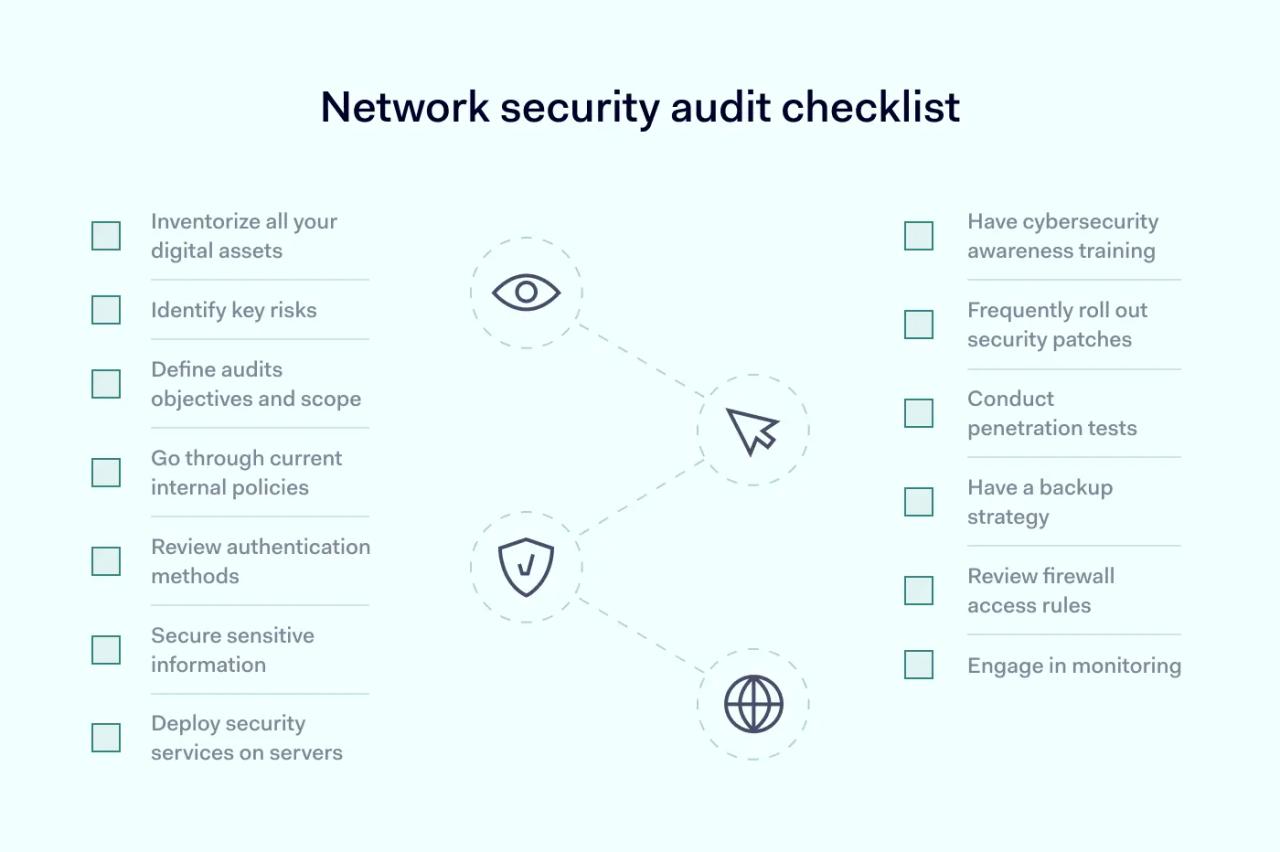
Don't forget that you don't have to do everything yourself, especially if you have the resources. However, if you don't want to rely on third parties and can do it independently, here's a network security audit checklist that should help you.
1. Inventorize all your digital assets
Identify all used devices and operating systems on your network. This includes:
- Organization-managed devices
- Unmanaged assets belonging to employees
- Network infrastructure devices like routers, switches, and firewalls
- IoT devices, such as smart thermostats, security cameras, and wearables
- Guest devices that connect to your network, like visitor laptops and smartphones
- Cloud-based resources and virtual machines
- Personal mobile devices used for work purposes
- Third-party service providers' equipment integrated with your network
The list of all these devices and access points will help you outline your organization's security perimeter. Pay special attention to various unsupervised methods employees might use to access company resources, as these can serve as potential backdoors into your network, especially personal mobile devices and remote access tools.
2. Identify key risks
Make a list of various cybersecurity risks that could be threatening your company. It's wise to include the most frequent business threats like:
Once you have identified these risks, evaluating security flaws in the right context becomes easier.
3. Define audit objectives and scope
It's crucial to set clear objectives and define the scope of your audit. This approach ensures you concentrate on the primary goals without getting lost in minor details. Here is what you should do:
- Define the audit scope: determine which parts of your network or systems will be examined.
- Aim for a comprehensive overview: get a good overall view of your current cybersecurity situation.
- Identify improvement areas: use the audit as a tool to spot weaknesses or gaps in your cybersecurity defenses.
In this way, an audit can serve as a method to identify the areas that need improvement.
4. Go through current internal policies
Revising your company policies can provide invaluable insights into your company's security. There should be a good justification behind the following:
- The usage
- Wireless network security
- Internet access
- Other policies
Better transparency in network security policy areas can have long-term benefits.
5. Review authentication methods
Leaked passwords can be a significant risk, especially if your employees tend to reuse them. To avoid password leaking, you can:
- Enforce strong passwords: ensure employees create strong and complex passwords.
- Add security layers: implement additional measures like two-factor authentication for enhanced protection.
- Mandate password updates: require regular password changes to improve overall security.
6. Secure sensitive information
Some assets hold the most sensitive data types, which the hackers target. Therefore, sensitive information should never be stored in an unencrypted form. How can you achieve it?
- Never allow unauthorized individuals to access it
- Restrict employees to the resources needed for their direct tasks
7. Deploy security services on servers
Your servers are crucial as they ensure network connectivity and store critical data. To maintain their integrity:
- Ensure proper configuration to allow only trustworthy connections
- Maintain a comprehensive server list detailing IP names, purposes, operating system versions, etc.
- This preparation aids in quickly restoring service in case of emergencies
8. Have cybersecurity awareness training
Integrating cybersecurity training into your onboarding process is essential. Awareness is key because employee actions can significantly endanger your organization's security.
- Employees need to understand common mistakes that jeopardize security.
- Conducting internal cybersecurity exercises can effectively gauge the susceptibility of employees to phishing by tracking who opens suspicious links.
- Investing time and effort to reinforce the notion that cybersecurity is everyone's responsibility is crucial for fostering a culture of vigilance.
9. Frequently roll out security patches
Keeping your software up-to-date is crucial for safeguarding your systems against cyber threats.
- Always update applications, operating systems, and other software to the latest versions.
- Apply timely patches to close vulnerabilities that hackers could exploit.
- Ensure antivirus applications are updated regularly to access the most current malware databases to detect malicious files effectively.
10. Conduct penetration tests
Penetration testing offers a unique perspective by simulating a hacker's approach, uncovering vulnerabilities that might be missed by solely concentrating on perimeter security.
- These tests help identify loopholes that could be difficult to detect with a narrow focus.
- Tools available can test applications both in their inactive and active states.
- Regularly reviewing the effectiveness of your current penetration testing methods is advisable to ensure they remain comprehensive and up-to-date.
11. Have a backup strategy
Having a robust backup strategy is like an insurance policy for your data, epitomizing the wisdom of being safe rather than sorry.
- Every company needs an emergency data backup plan.
- Regular audits of the backup process are crucial to ensure its effectiveness
- Any gaps in the backup strategy can significantly extend the data recovery time or render data recovery impossible.
12. Review firewall access rules
A firewall serves as the primary checkpoint for all inbound and outbound network traffic, acting as a critical line of defense.
- Proper configuration of firewall rules is essential for an effective barrier against cybersecurity threats
- Close any open ports that are not in use and revoke permissions for unsupervised connections
- Segmenting your internal network is a great tool for enhanced control over internal traffic, further securing your network
13. Engage in monitoring
Monitoring and analyzing past logs are crucial tools for enterprise security management.
- Implement a company-wide system for collecting and reviewing logs to ensure thorough oversight.
- Keep an eye out for new devices on the network, verifying their identity and ownership promptly.
- Regularly cleaning up inactive accounts and devices from the system is a proactive step toward maintaining a secure environment.
Network security audit challenges
No two enterprises will have the same challenges if you're wondering what potential bottlenecks could be when performing network security audits. For some, the audit scope will be very high, as they're huge enterprises, making the audit process more time-consuming and expensive. For others, the main problems will be the lack of knowledge to perform threat detection or to analyze the audit data.
As with many projects, you'll need discipline and willingness to achieve a better cybersecurity status. Even if you're on a very limited budget, there are many cost-saving opportunities. The focus should be on making gradual improvements that would bring value to the organization for years to come.