Malware is evolving. Advanced malware hides its identity to bypass security measures, concealing itself deep within target networks until it is ready to launch attacks. Advanced malware protection (AMP) is the only dependable way to counter these next-generation threats.
This article will introduce AMP and explore how it works. We will discuss different types of AMP and suggest practical ways to implement advanced malware protection in your organization.
Advanced malware protection definition
Advanced malware protection (AMP) uses machine learning, artificial intelligence, and behavioral analysis to safeguard networks against advanced threats. AMP builds on existing malware detection and removal methods, detecting advanced threats that bypass older security tools.
What is the difference between malware and advanced malware?
There are many differences between traditional malicious software and advanced varieties.
Advanced malware is a type of malicious software that evades standard cybersecurity measures, employing techniques like polymorphism to bypass signature-based detection. Meanwhile, rootkits and bootkits embed advanced malware deep within target networks.
Advanced malware also tends to include encrypted command and control capabilities. This allows attackers to launch precise attacks and control data extraction or system compromises, while encryption shields their activities and complicates advanced threat detection.
Advanced threats are engineered to move laterally within networks via techniques such as Pass-the-Hash. This gives attackers freedom to roam and discover valuable data. Some variants also detect mitigation measures such as sandboxing. They may also use cloaking tools to contaminate analytical data, making triage difficult.
Traditional malware does not possess these capabilities. Older strains of malware tend to have consistent signatures and attack profiles, which makes detection easier. They are susceptible to detection and analysis methods, enabling rapid responses. And they rarely become embedded in targeted devices, making removal simpler.
How does advanced malware protection work?
Given the threat posed by next-generation threats, advanced malware protection is essential. AMP tools counter advanced threats with several tools and features, strengthening network defenses against the latest malware agents. Core features include:
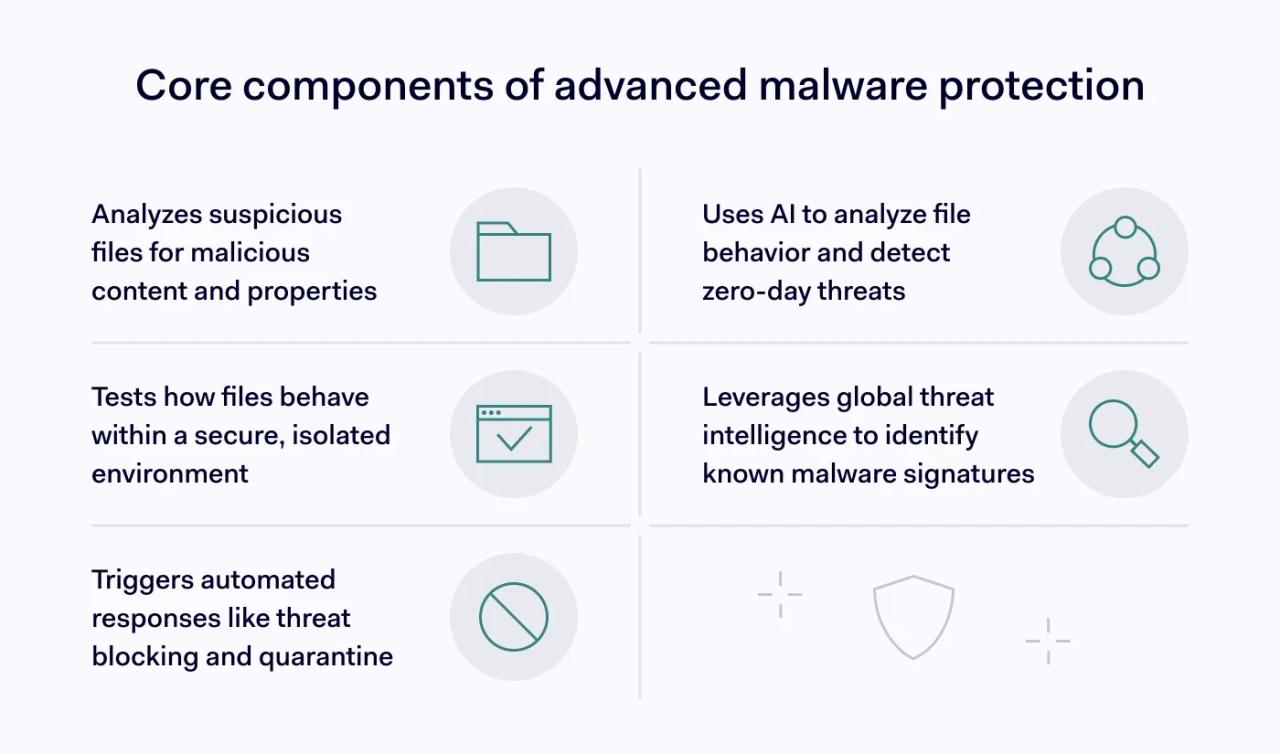
- Analyzing suspicious files: File analysis screens incoming files to detect malicious content. Static analysis checks file properties, including headers and metadata.
- Behavior analysis: Analytics tools use machine learning to compare file behavior with known malware agents. AI tools can detect malicious activity, such as encryption injection, without requiring existing malware signatures. This is a valuable asset when neutralizing zero-day threats that systems have not yet encountered.
- Secure sandboxing: Sandboxing goes deeper, assessing how files behave in safe environments (for example, whether they execute malicious actions such as registry calls). Sandboxes may also carry out file emulation, running files to assess payload execution.
- Threat intelligence: Advanced malware protection leverages global threat databases containing malware signatures and attack profiles. Analytical tools use intelligence to identify threat actors and potential attack techniques.
- Automated responses: AMP may trigger automated threat blocking and quarantine measures. It can also integrate with extended detection and response (XDR) or endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools to ensure consistent threat mitigation.
These techniques contrast with malware and anti-virus tools based on signature detection. Signature detection continues to play a critical security role. However, cybersecurity solutions must look beyond signatures to guard against dynamic advanced threats.
Types of advanced malware protection
Advanced malware protection takes several forms. Organizations should choose a threat detection solution that suits their IT landscape and data protection requirements:
Behavioral analysis tools
These advanced malware protection tools analyze user and file behavior to detect suspicious activity. Security tools apply heuristic techniques to compare real-time activity with secure baselines. Security teams can identify unknown threats linked to zero-day exploits. Behavioral analysis is also good at exposing polymorphic agents with dynamic signatures.
Endpoint detection and response (EDR)
EDR protects network endpoints against advanced malware threats. Agents located on endpoints (including web servers, cloud portals, user devices, and Internet of Things sensors) scan for potential threats and deliver alerts to centralized security consoles.
Extended detection and response (XDR) enhances EDR by integrating real-time detection with forensic analysis capabilities. This helps to reduce false positives while flagging advanced threats and providing comprehensive threat data to inform responses.
Cloud-based AMP
These advanced malware protection solutions reside on cloud deployments (and are often provided as a service by cloud vendors).
Cloud-based solutions scale easily, covering new cloud assets as they come online. Vendors can also provide timely updates, ensuring security coverage adapts to evolving threats. Users do not need to invest in on-premises security tools, cutting the cost of guarding against advanced malware.
AI and machine learning AMP
Sophisticated advanced malware protection leverages AI and machine learning to stay ahead of evolving malware threats. AI/ML constantly scans for unusual file or user behavior and analyzes data from multiple sources (including network endpoints, applications, and external threat intelligence).
AI-based advanced malware security also automates security functions, reducing the need for manual inputs and cutting the risk of human error.
Note: Several critical technologies complement the AMP variants listed above. For example, next-generation firewalls enable deep packet analysis and incorporate behavior monitoring. Intrusion detection systems monitor network traffic for suspicious patterns. Zero Trust controls also limit lateral movement by applying the principle of least privilege.
Advanced malware protection best practices
Advanced malware infects targets without warning and can lead to data breaches, ransomware attacks, and regulatory penalties. Companies need measures to safeguard assets against advanced threats. Following the best practices below will improve your defenses and block threats before they inflict damage.
- Apply AMP to all network devices: Advanced malware protection must cover every endpoint and cloud instance. Use endpoint scanning tools to detect all internet-facing devices, including mobiles, tablets, laptops, and servers.
- Map traffic flows and data locations: AMP must also screen traffic flowing across the network perimeter and between network devices. Mapping data flows helps you secure critical traffic, including emails, file transfers, and financial transactions.
- Enable automated ML/AI tools: Advanced malware protection tools with AI features save time by automating threat scanning. They also reliably detect zero-day threats. Choose a solution that exploits cutting-edge techniques to ensure optimal threat detection.
- Regularly update all applications and firmware: Advanced malware targets outdated software. Use automated patch management tools to deliver timely updates. Ensure you update AMP solutions as well, and audit vendors annually to verify your security tools remain effective.
- Use a multi-layered threat protection approach: Protecting against advanced threats requires multi-layered security measures. The best threat protection solutions combine AI threat detection with DNS filtering to block unauthorized content and download protection to scan incoming files.
- Employ Zero Trust access management: Containing advanced malware is essential. Apply network segmentation to guard high-value assets. Only authorize access to users with a legitimate business justification, and screen user identities at every stage in line with Zero Trust principles.
- Combine AMP with threat intelligence platforms: AMP and intel platforms work together to deliver relevant alerts and information about critical threats. This combination helps analysts triage alerts and choose the correct response.
Guard against emerging threats with advanced malware protection
In the dynamic cybersecurity landscape, change is the only constant. Static ransomware agents and Trojans are being replaced by dynamic persistent agents. As malware develops, legacy security tools struggle to detect and neutralize advanced malware threats, putting data and network systems at risk.
Advanced malware protection provides a solution. AI and machine learning assess user behavior and suspicious files. Security tools sandbox threats for secure analysis and expose embedded threats wherever they reside. The result is advanced protection against the most dangerous cyber threats.
