SOC 2 reporting is essential for companies that handle customer information or process data as third parties. But what does this compliance framework involve, and how is a SOC 2 report produced? This article explains everything you need to know about SOC 2 reports.
SOC 2 report definition
A System and Organization Controls (SOC) 2 report is an assessment of an organization's digital security posture by a certified public accountant (CPA). SOC 2 reports assess data security, integrity, confidentiality, privacy, and availability controls. Compliance assures clients that service organizations meet the security standards to avoid unauthorized disclosure and data breaches.
Key SOC 2 reporting sections
SOC 2 reports detail the makeup and effectiveness of service organization control setups. Reports follow a standard structure for all organizations, and readers can expect to encounter the sections below.
Section 1: Management assertion
The service organization completes the first section. The management assertion confirms that the organization being audited designed its security controls and implemented them within the audit window. In the case of Type 2 audits, the assertion states that the organization implemented continuous compliance measures during the reporting period.
Section 2: The auditor's report
This section is the heart of a SOC 2 report. The auditor's report presents the findings of the SOC 2 audit.
The auditor officially judges whether the organization has met SOC audit requirements. There are three possible outcomes at this point:
- If the verdict is qualified, the auditor found general compliance with some minor improvements. The auditor will confirm compliance within a set period following corrective actions.
- If the verdict is unqualified, the auditor found no notable compliance problems. Service controls conform to SOC 2 guidelines. The company has achieved certification within the monitoring period.
- Verdicts can also be adverse. The auditor found significant compliance failures. In these cases, organizations usually need a fresh audit process.
Auditors delivering qualified or adverse opinions provide a reason for their criticisms. This is often due to a mismatch between systems described by the service organization and operational controls. Auditors express their opinion that the organization cannot assure clients regarding data protection. Further action is essential.
Section 3: The system description
System descriptions supply detailed information about the organization's security controls and policies. The organization completes this section, which enables auditors to compare written descriptions with controls when arriving at their opinions.
The scope of the descriptions section varies depending on the service organization. Areas requiring descriptions could include:
- The nature of the organization's business operations
- Commitments or assurances made to clients
- How operations relate to specific Trust Service Criteria
- User entity controls such as access management, authentication, or firewalls
- Components of the Information Security Management System (ISMS)
- Subservice controls used by the organization
- Incident response plans and controls
- System changes made during the audit window
System descriptions enable auditors to analyze whether a service organization meets its contractual obligations and meets AICPA's TSCs. The section must contain enough detail to compare the claims made by organizations with operational controls.
Section 4: Trust Service Criteria and audit testing
This section is generally the most in-depth of the whole report. Section 4 combines security controls from the system description with feedback from the auditor. This feedback assesses whether the controls perform their assigned functions in line with Trust Service principles.
Section 4 presents the results of audit testing. For example, the findings might document that "firewalls blocked unauthorized access and access management systems admitted authorized users, without compromising operational requirements agreed with clients."
In addition to documenting testing, this section flags up problems and highlights necessary corrective actions.
Section 5: Additional information
The organization being audited completes the final section. Adding further information is completely optional. Companies are free to add information about future compliance projects. They might explain why auditors have detected compliance gaps or issues with internal controls. This part is an opportunity to supply context - provided it remains focused on SOC 2 compliance issues.
Why SOC 2 stands out among other SOC reports
The SOC compliance family includes three tiers of SOC report. However, SOC 2 has a strong reputation among data processors. There are a couple of reasons for the superiority of SOC 2 over other AICPA standards.
Most importantly, SOC 2 deals with broad cybersecurity and data protection issues. Auditors assess data security. But they also consider availability, data integrity, confidentiality, and data privacy. A SOC 2 report captures a lot of relevant information to assure clients and promote security-conscious service organizations.
SOC 2 combines detail with flexibility. Organizations can tailor reports by selecting TSCs. They can opt for a point-in-time SOC 2 Type 1 report. This is often a preferred entry point into the SOC framework. As they improve their internal controls, companies can graduate to SOC 2 Type 2 reports - assessing continuous compliance.
The integral role of CPAs in ensuring accurate SOC 2 audits
Certified Public Accounts (CPAs) produce SOC 2 reports. CPAs are AICPA-approved (the organization that maintains SOC standards). Each approved auditor has an intimate knowledge of SOC 2 criteria and reporting guidelines.
Skilled CPAs understand the industry-specific needs of companies. They adapt audits to unique business objectives, finding correct methods to test data controls. CPAs are also risk management specialists. Auditors identify data security or privacy risks and test internal controls to ensure they manage risks effectively.
A good CPA uses their skills and knowledge to make reasonable judgments without being excessively lenient. And they need exceptional communication skills to cooperate with organizations throughout the audit period.
How stakeholders depend on SOC 2 reports
SOC 2 reporting is a critical process in many digital industries. This applies to companies, customers, and regulators alike. Any organization that transfers data to third parties or processes customer data can benefit from SOC reports.
Business partners
Cloud-based digital collaborations are routine. Companies often share marketing information or expertise to tap new audiences. However, sharing data can lead to data breaches and privacy risks.
Business partners use SOC 2 reports to verify security credentials. Audit findings allow companies to collaborate safely and capitalize on partnerships.
User organizations
Companies often use software-as-a-service providers to process payroll data, handle accounts, or manage customer relationships. However, every data transfer to a cloud third party adds new security risks.
Companies use SOC 2 reports to assess third parties. Qualified auditors assure clients that CSPs will respect user privacy and data integrity. Reports provide data security assurance - opening new cost-saving opportunities while ensuring data breach prevention.
IT teams
Internal IT teams or executives can use SOC 2 reports to build stakeholder trust. SOC 2 report feedback assesses security controls and data practices. IT teams can use the findings to refine their ISMS or request resources. Executives can expand their strategic awareness and improve organizational cybersecurity.
Regulators
Regulators use SOC 2 reports to assess compliance with data privacy and security laws. For example, EU regulators may consult a SOC 2 report when investigating privacy breaches. SOC reporting provides a ledger of controls with expert feedback about their effectiveness.
Regulators may also look for SOC 2 reports when assessing a data controller's due diligence. SOC reports suggest that companies factor regulatory compliance into third-party arrangements. The absence of a SOC 2 report raises concern that an organization handles data irresponsibly.
Unpacking the depth of SOC 2 Type 1 vs. Type 2
There are two tiers of SOC 2 report: Type 1 and Type 2. The two SOC 2 report types have significant differences. They also serve slightly different purposes. So it's important to understand these differences when starting a SOC 2 compliance journey.
- SOC 2 TYPE I. SOC 2 Type 1 reports produce a point-in-time description of an organization's internal controls. In this type of SOC 2 report, auditors list controls but do not provide detailed testing feedback. The auditor writes an attestation instead. This section evaluates whether controls met AICPA standards within the audit period.
- SOC 2 TYPE II. SOC 2 Type 2 reports assess compliance over 3-12 months. Auditors test controls regularly. The internal controls audit seeks evidence of continuous monitoring. Reports include testing data and delivering an in-depth analysis of how closely the organization complies with Trust Services Criteria.
Type 1 reports take less time to complete. Achieving compliance is easier due to the absence of continuous monitoring. For these reasons, Type 1 assessments suit companies needing basic security assurance or a baseline for further compliance work.
Feature | SOC 2 Type 1 | SOC 2 Type 2 |
|---|---|---|
Objective | Evaluates the design of security processes at a specific point in time | Examines the operational effectiveness of those processes over a period of time |
Focus | Design effectiveness | Operational effectiveness |
Timeframe | A snapshot in time | A minimum of six months |
Audit Scope | Assesses if controls are properly designed to meet Trust Services Criteria | Assesses the operational effectiveness of controls over a period |
Report Use | To prove a system is designed with the necessary security controls at a specific date | To demonstrate how effectively a system operates over time, showing control effectiveness |
Audience | Potential and current customers looking for assurance at a point in time | Customers needing detailed assurance of ongoing operational effectiveness |
Tech start-ups with limited resources are good candidates for Type 1 assessments. The same applies to small-scale eCommerce firms that want to assure customers but do not require extensive SOC auditing. In both cases, Type 1 audits balance assurance, time, and cost.
Type 2 reports are more detailed, but also more time-consuming and expensive. They provide robust assurance for user organizations and actionable information for internal use. Type 2 assessments suit organizations with mature security environments. They are essential for companies with low risk tolerance. Health insurers or financial brokers are good examples.
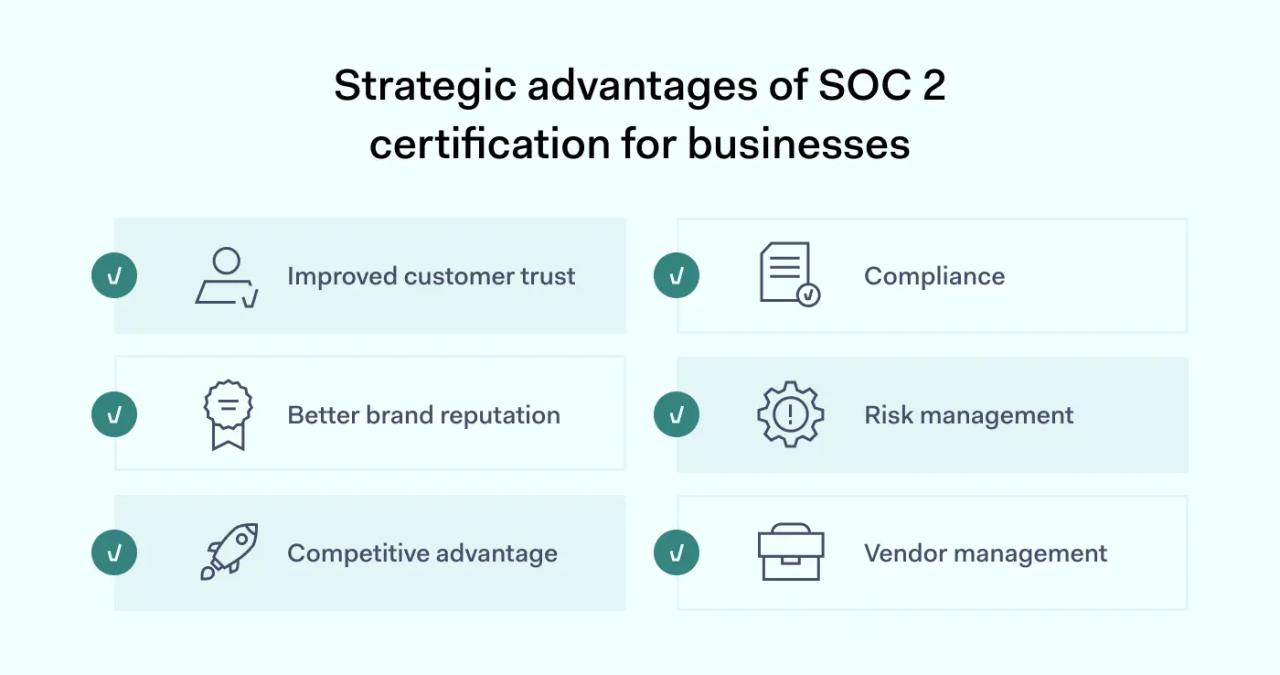
Strategic advantages of SOC 2 certification for businesses
SOC 2 certification is much more than a paper achievement. A positive SOC 2 report delivers:
- Improved customer trust. Clients seek companies that protect personal and financial data.
- Better brand reputation. SOC certification confers security credibility, positioning companies as leaders in their field.
- Competitive advantage. Fewer data breaches and disclosures improve customer loyalty and attract clients from less reliable competitors.
- Compliance. SOC 2 standards help companies comply with demanding regulations like GDPR or HIPAA. Compliance also reduces the risk of regulatory penalties.
- Risk management. The SOC 2 audit process encourages companies to adopt systematic risk analysis. Organizations learn their data security risks and how to take appropriate action.
- Vendor management. SOC 2 reports are like passports to easier vendor partnerships. Partners are much happier to deal with responsible companies that adopt compliant data practices.
Above all, SOC 2 makes companies leaner and more security-conscious. In a world of frequent data breaches and cyber-attacks, compliance is a critical ally that gives organizations an invaluable advantage.
Conclusion
SOC 2 is one of the most respected and versatile security compliance frameworks. As we've seen, obtaining a SOC 2 report has many benefits. The importance of SOC is only growing as companies embrace digital transformations and technologies like AI or the Internet of Things.
In the digital world, companies rely on partners to keep data safe. SOC 2 provides assurance, enabling secure collaborations. The future will surely see new developments as AICPA adapts to innovation. Stay informed, research SOC updates, and always be prepared to renew your SOC 2 certification.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and not legal advice. Use it at your own risk and consider consulting a licensed professional for legal matters. Content may not be up-to-date or applicable to your jurisdiction and is subject to change without notice.
