The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a set of data privacy regulations that guide businesses on how to keep individuals' personal data secure. These data security rules apply to any business that handles the data of EU citizens. Organizations that fail to comply with GDPR risk severe penalties of up to 4% of their annual turnover.
GDPR provides a detailed framework that covers how businesses may handle, store, or transmit personal data. However, it is not explicit in how organizations must carry out these guidelines. To ensure all employees understand the importance of keeping individuals' personal data private and secure, companies develop data protection policies. These policies help the company demonstrate compliance, simplify GDPR for their employees and ensure that personal data is kept secure.
Key takeaways
- If your company is a data controller, a data protection policy is crucial for demonstrating GDPR compliance and prioritizing data security.
- The policy simplifies GDPR requirements for employees, enabling them to understand and implement its contents.
- Having a data protection policy shows a company's commitment to preventing data breaches and is necessary for maintaining thorough compliance documentation.
- The policy should include information on the purpose, key terms, scope, principles, data subject rights, and the appointment of a data protection officer.
- Successful implementation hinges on educating the workforce about GDPR.
What are Data Protection Policies?
A data protection policy is an internal document that provides guidelines on how a company will protect consumer data. The purpose of the policy is three-fold:
- To ensure company-wide GDPR compliance
- To educate employees about data security and their responsibilities
- To protect individual's personal data
The data protection policy is most relevant to those that handle consumer data but applies to the whole organization in general.
A comprehensive policy will include aspects like:
- The purpose and scope
- Core definitions, such as data processing or personal data
- The GDPR principles, such as data minimization
- Lawful processing of data
- Roles and responsibilities of employees and other stakeholders
- Data breach processes
- Data subjects' rights, like the right to be forgotten
- Record keeping to align with audit requirements
- Contact details of the company and specifically the data protection officer
Benefits of Having a Data Protection Policy
Business leaders often struggle to prioritize compliance issues in addition to their operational duties. However, the majority do understand that the benefits of implementing information protection guidelines outweigh the efforts.
Avoiding non-compliance penalties
Any organization that works with EU citizens' data must comply with the General Data Protection Regulation. Those that don't risk major fines. Implementing a data protection policy will help everyone in the business prioritize data security. With the average global data breach costing companies $4.45 in 2023, following the GDPR privacy guidelines is a must.
Laying down fundamental compliance evidence
Companies must be able to demonstrate their GDPR compliance easily. The foundation layer that shows a company is in line with the regulations is having a data protection policy in place. This shows that the organization has the basics in place and does not see compliance as a mere tickbox exercise. It's absence could be a viewed as red flag by regulators.
Minimizing the risk of data breaches
The GDPR framework doesn't say how businesses should implement the regulations. However, an organization's security policies and procedures focus on how to keep consumer data safe. Including a data protection policy in a company's security measures will reduce the likelihood of a data breach.
Simplifying GDPR for employees
Everyone in the workforce needs to work safely with consumers' personal data. But employees have different levels of experience and understanding regarding technical issues like GDPR. It's important for companies to simplify these matters for them by creating policies and procedures that they can understand. And most importantly — apply.
Building trust with customers
Customers want to know that businesses keep their personal data safe at all times. In fact, in a recent Cisco survey, 90% of the respondents said they wouldn't buy from a company that didn't safeguard it's data. Organizations that implement a data protection and privacy policy demonstrate that they take data privacy and security seriously.
How to create a GDPR-Compliant data protection policy
Your data protection policy expresses your organization's commitment to keeping personal data out of the wrong hands. The policy doesn't detail how your business will implement the GDPR principles but explains how GDPR applies to your particular business.
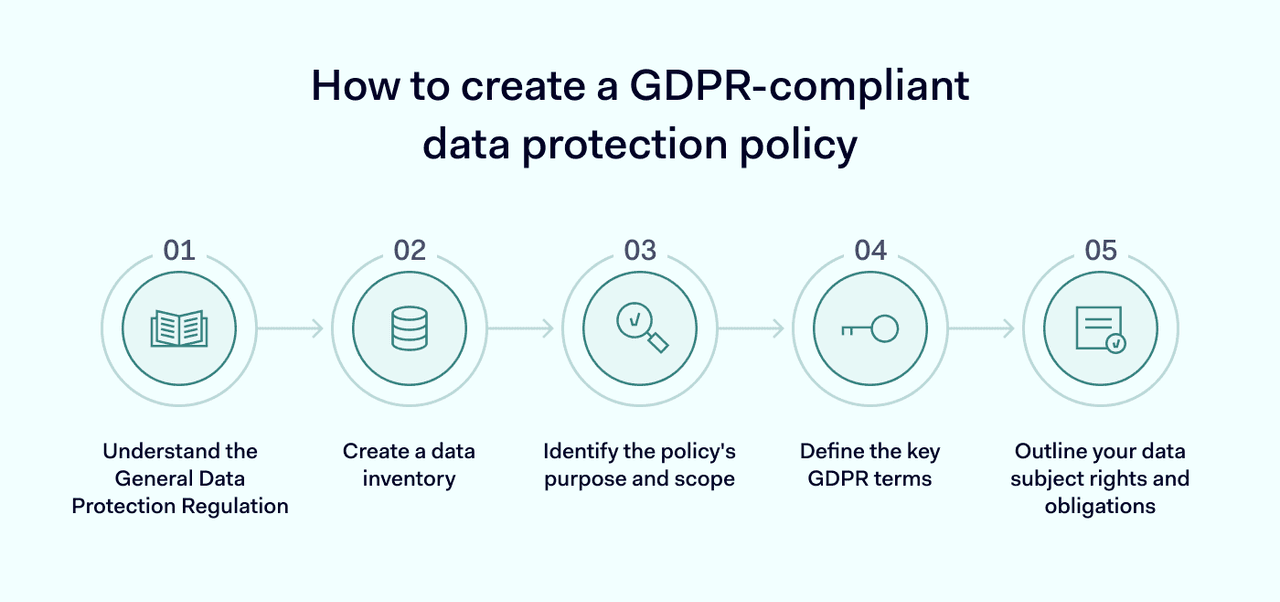
1. Understand the General Data Protection Regulation
The best approach is to begin with a solid understanding of GDPR. This includes how it's relevant to your business and industry. Plus, ensuring that you keep up to date with any regulatory updates. Companies that work with a lot of personal data must appoint a data protection officer (DPO). The DPO is responsible for helping the business remain GDPR compliant.
2. Create a data inventory
Businesses use and store data across many different departments, in different formats and in different locations. When it comes to consumers' personal data, the organization needs to know exactly what personal data is stored, where it's stored and what it's used for. Creating a data inventory is essential for maintaining detailed GDPR compliance records.
3. Identify the policy's purpose and scope
The purpose and scope of the policy will help organizations know why this particular policy document is important. Plus how it affects them and the broader business. Since every business is different, a generic purpose and scope may not work for all. For instance, the scope of a major global enterprise will be far more complex than that of a startup, though both deal with peoples' personal data.
4. Define the key GDPR terms
Not every employee is technically minded. That's why it's important to include the definitions of the key GDPR terms, such as consent and accountability. Once they understand what the main terms mean, it'll no longer be a stumbling block to understanding and applying the data protection policy.
5. Outline your data subject rights and obligations
A data subject refers to the person whose data you're working with. Data subjects have specific rights under the GDPR rules. These should also be included in your policy to show how you'll uphold those rights. For example:
- Right to be forgotten - erasing personal data when it's no longer needed
- Right to object - processes for data subjects to object
- Right of access - sharing their data with them when they request it
- Right to rectification - you'll correct or update their personal details
- Right of portability - sharing their data in a usable format for other data controllers
Implementation of Data Protection Policies
A data protection policy is only useful if it is implemented. It's no use creating a detailed document and then not taking the next step - getting staff to understand and use it.
You can kickstart your policy implementation by:
- Making sure you've got data security and compliance champions at all levels of the organization from execs to junior levels.
- Promoting collaboration across the core teams involved, including IT, compliance and security staff.
- Communicating regularly about GDPR to the whole company sharing best practices and lessons learned so everyone can learn from each other.
- Training employees on GDPR and their responsibilities by including it in their employee handbook.
- Reviewing and updating the policy to keep it relevant and compliant. For instance, after a merger, data management workflows may look different.
Once the policy is implemented, it is the Data protection officer's (DPOs) responsibility to ensure that everyone is following the procedures and that the company has proper safeguards in place.

Weaving accountability into the GDPR policy
A business is accountable to many stakeholders, such as their employees and customers. In terms of GDPR, accountability refers to how the company takes responsibility for handling personal data. In this instance, it is accountable to it's data subjects, employees and to the regulatory authorities.
Businesses need to demonstrate their accountability obligations through technical and organizational measures. These could include maintaining detailed records, having documented processes and procedures, and employing a data protection officer. A data inventory is also a good place to start when demonstrating accountability.
Protecting individuals' personal data is the responsibility of every employee who works for a data controller. Simplifying data protection and privacy compliance laws through a data protection policy, for instance, is key to organization-wide compliance. Companies that fail to prioritize data security risk big penalties and losing customers if a data breach occurs.
Yet, with the right technology and support, it's possible to develop and maintain a comprehensive data protection policy and other General Data Protection Regulation requirements. By partnering with experts in the field, you can work together to keep personal data out of the wrong hands.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and not legal advice. Use it at your own risk and consider consulting a licensed professional for legal matters. Content may not be up-to-date or applicable to your jurisdiction and is subject to change without notice.