Constant connectivity and online communication form the backbone of today's business. This makes network security one of the most important areas for enterprises to consider. Naturally, network security devices like firewalls get the most spotlight due to their functionality.
As there are many types of firewalls, we'll focus on the application-level gateway firewall in this article. Providing comprehensive protection against malicious traffic while allowing users to access external computers and network applications helps keep the security airtight.
Definition of an application level gateway firewall
An application gateway (ALG) firewall is a type of firewall that protects the application layer of the OSI model. It's deployed on a computer's internal system and filters incoming node traffic by examining and controlling application session initiation. In other words, an ALG firewall acts as an intermediary between external users and the main server, controlling traffic and preventing malicious attempts to gain access.
How does an application level gateway firewall work?
Most firewalls filter incoming data packets based on port numbers and internet protocol. Meanwhile, an ALG firewall provides an additional layer of security by filtering incoming traffic using a proxy to establish connections for remote users. The client relies on a proxy server to interact with the destination behind the firewall. This hides and secures individual computers on the network behind the firewall.
Two connections are in effect here: one is between the client and the proxy server, and another is between the proxy server and its destination. In this model, the proxy makes all packet-forwarding decisions. Incoming data packets are filtered at the application OSI layer.
Within this session between the remote user and proxy application, a separate sub-session is created between the proxy application and the internal internet server. The remote client sends a request to the proxy, while it acts as an intermediary with the internet server. Finally, the result is returned to the remote user if the exchanged packet meets the set policies.
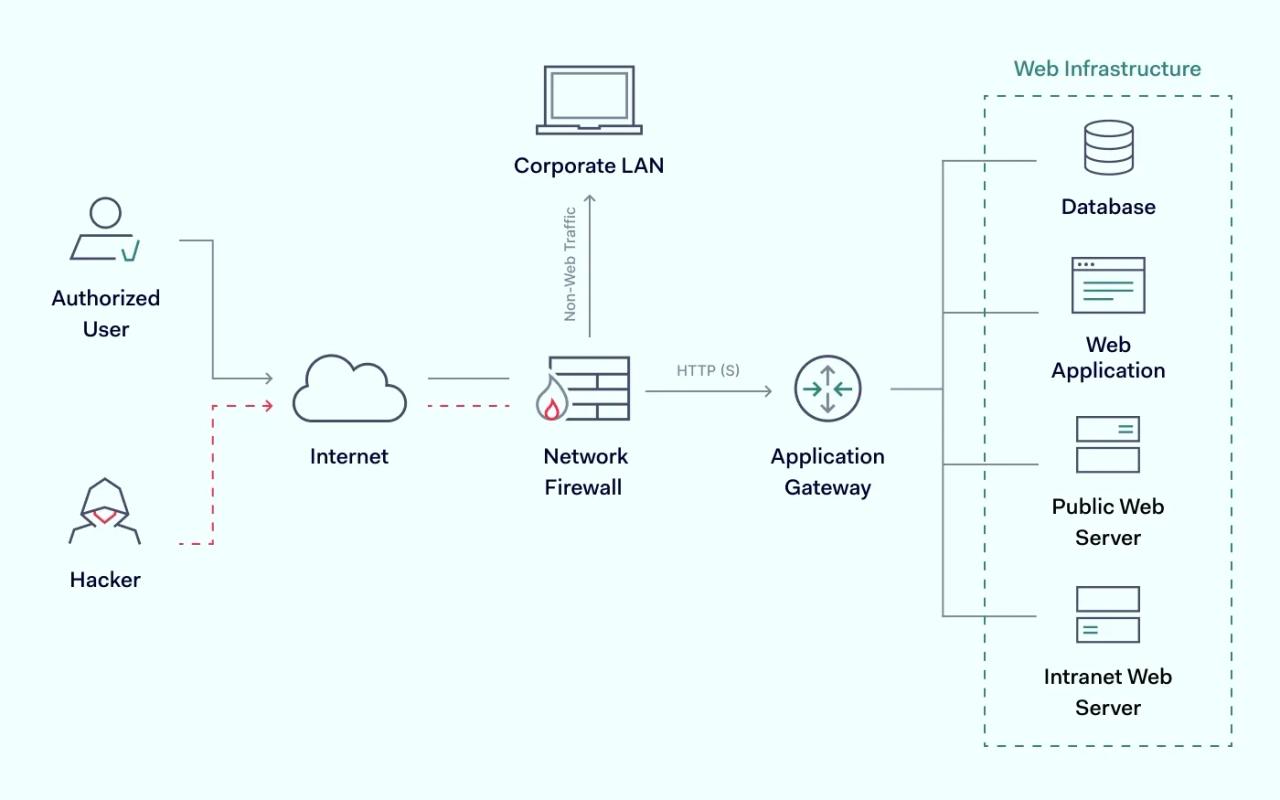
The main benefit of using an ALG firewall over traditional packet filtering systems is that it's not a direct network connection. The remote user doesn't access the network directly, only an intermediary does that, which helps to shrink an attack surface. It also helps to allocate resources and control application session initiation. Using it to prevent users from accessing certain network applications or web pages.
Benefits of using an application level gateway firewall
ALG firewalls can benefit organizations looking to secure their networks and improve network performance. This solution can bring much value if you're looking to protect your organization from cyber threats or optimize traffic load.
1. Increases security
ALGs provide an unparalleled degree of security by examining the content of the packets that pass through them rather than just headers. This allows a much deeper level of inspection, detecting specific applications and protocols and applying various security policies and controls based on the application's needs.
2. Allows traffic logging
Logging the connection of a specific server is much easier than logging the logs of all enterprise's endpoints separately. An intermediary server stores all logs of every transaction on the server, allowing IT teams to review granular details of all access attempts. This can help to detect employee usage habits and identify potential threats.
3. Supports content caching
In today's digital environment, optimal application performance is paramount, which is where content caching comes into play. This allows the ALG firewall to cache frequently accessed content, so it can be retrieved locally instead of fetching from the original server when requested.
4. Network performance improvements
Application gateway firewalls can distribute incoming traffic across multiple backend servers to ensure that no single one is overloaded. For users, this means better uptime, ensuring that the service is always up and running when needed. In addition, ALG can offload SSL processing from the backend servers, freeing up resources and implementing performance.
5. Layered access model
With ALG, web applications are protected with additional barriers that push the threats further away from the organization's network. This provides multiple layers of protection, making it much more difficult for attackers to bypass security measures to access sensitive data or systems. Organizations can exploit this by preventing attacks from impacting their web applications.