Summary: Learn why healthcare data security is critical, the top threats, and practical strategies healthcare organizations can use to protect patient data.
Imagine an attacker quietly gaining access to sensitive patient information in your hospital network—reading lab results, personal health information, insurance details, and even payment data, undetected for weeks. For many healthcare organizations, this is not a hypothetical scenario but a daily concern.
In a world driven by electronic health records and digital transformation, healthcare data security has become critical for protecting patient privacy, maintaining operational integrity, and complying with strict regulations while building patient trust.
In this article, we’ll walk through what makes healthcare data security uniquely challenging and why it’s critical to get it right—from understanding the most common threats to implementing practical strategies that protect patient data.
What is healthcare data security?
Healthcare data security refers to the policies, practices, and technologies healthcare providers and companies use to protect electronic health records (EHRs), personal health information (PHI), and other sensitive patient data from unauthorized access, corruption, or theft.
It ensures that patient data security aligns with regulatory requirements, organizational goals, and patient privacy expectations.
Healthcare data security involves implementing layered security measures, including secure networks, encryption, role-based access control (RBAC), multi-factor authentication (MFA), and continuous monitoring to protect healthcare data across all systems and endpoints.
Why healthcare data is a growing cybersecurity concern
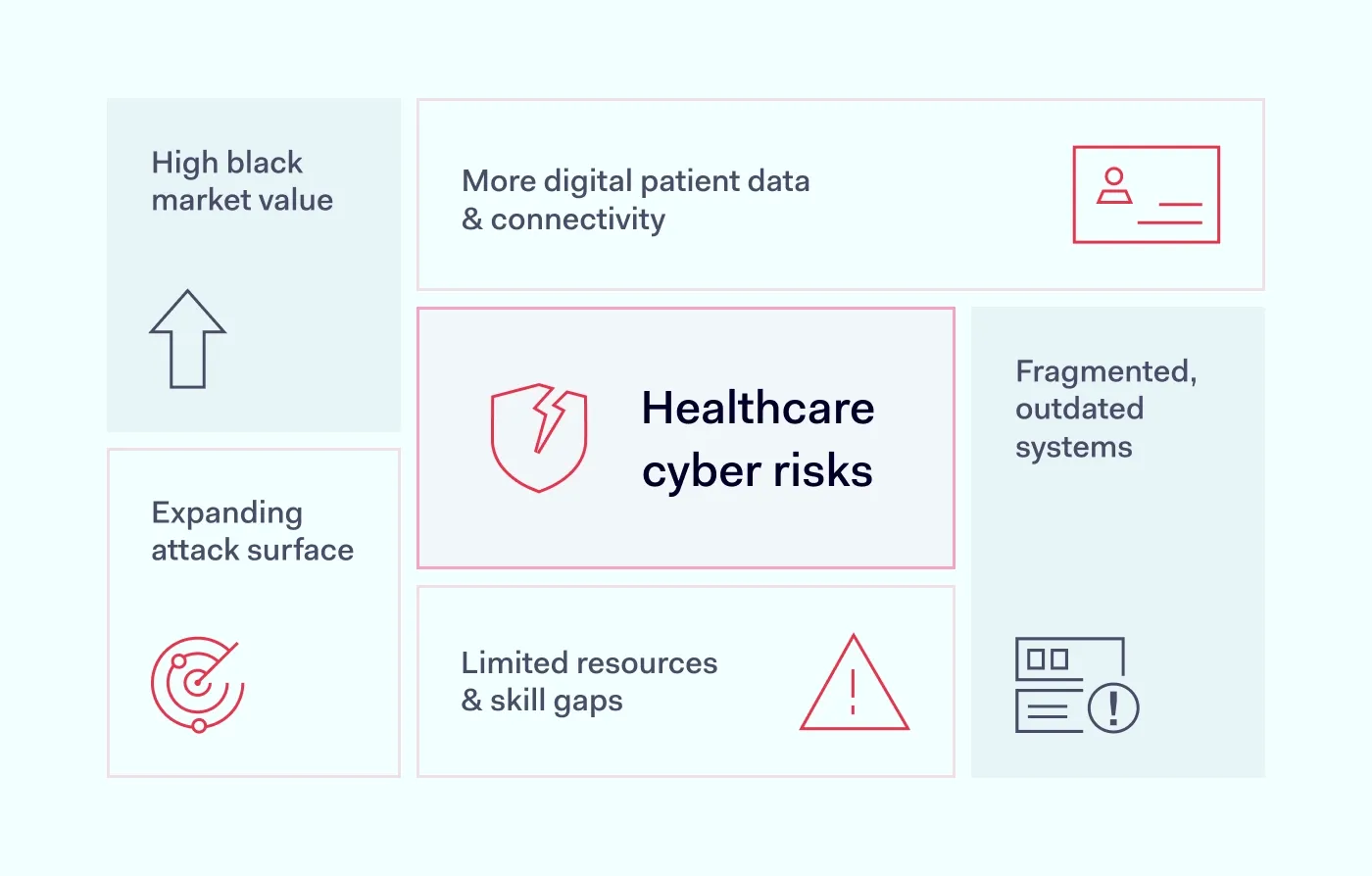
The healthcare industry is especially exposed to cyber threats that are becoming more advanced and frequent. While the number of data breaches continues to rise, several reasons make healthcare data security harder to maintain:
Surge in digital patient data & interconnectedness
The widespread adoption of EHRs, coupled with the rapid expansion of telehealth services and remote patient monitoring, has dramatically increased the volume of sensitive patient data stored, processed, and transmitted digitally.
Every new digital tool helps patient care, but also gives attackers more points to target. The amount of valuable data makes healthcare organizations attractive targets for cybercriminals.
Fragmented systems & outdated infrastructure
Many healthcare providers still use old systems that were not built with modern cybersecurity in mind. These outdated systems often lack security features, have known weaknesses, and are hard to update or patch, making them easy targets for bad actors.
Replacing or upgrading these systems can be expensive, so many healthcare organizations struggle to modernize their cybersecurity.
High value of healthcare data on the black market
Unlike credit card numbers, which can be quickly canceled, PHI and insurance data are incredibly valuable on the black market. They can be used for various illicit activities, including identity theft, insurance fraud, and even medical fraud, for years.
This high street value makes healthcare organizations exceptionally attractive targets for financially motivated cybercriminals, leading to an alarming number of data breaches—only in May 2025, 59 breaches were reported in the U.S. healthcare sector, affecting 1.8 M individuals.
The average cost of a healthcare data breach is significantly higher than in other sectors, reflecting the sensitive nature of the data involved.
The expanding attack surface
The healthcare ecosystem is incredibly complex, with healthcare organizations relying heavily on a vast network of third-party vendors for everything from billing and IT services to specialized medical devices. If not properly secured, each third-party connection represents a potential entry point for attackers.
Furthermore, the growing use of IoT medical devices—from smart infusion pumps to remote monitoring sensors—introduces new vulnerabilities. Many of these devices are not built with robust healthcare data security in mind, creating a wider attack surface and increasing the risk of data breaches.
Resource constraints & skill gaps
Despite the critical nature of their data, many healthcare organizations operate with limited cybersecurity budgets and a lack of skilled cybersecurity professionals to manage it. This makes it harder to implement, maintain, and continuously update the advanced security measures necessary to keep pace with modern threats.
The ability to invest in cutting-edge healthcare data security tools and retain top talent is often a challenge.
Key regulations in healthcare data protection
To ensure patient data security and privacy, healthcare organizations must comply with several key regulations:
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA): Establishes national standards for protecting sensitive patient information.
Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act (HITECH): Encourages healthcare providers to adopt electronic health records while strengthening the privacy and security protections under HIPAA.
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): This regulation applies to healthcare providers processing EU residents' data and requires strict data protection measures.
State-specific privacy laws: Regulations like the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) may also apply, emphasizing patient privacy and data security practices.
These regulations are designed to ensure healthcare data protection, requiring healthcare organizations to adopt robust security measures and implement strong data protection practices.
Related articles

Maciej SikoraJul 15, 20257 min read

Anastasiya NovikavaDec 5, 202510 min read
Top security threats to healthcare organizations
Various cybersecurity firms and annual industry reports confirm healthcare as a prime target for specific attack types like ransomware and phishing. Reports from cybersecurity firms like Proofpoint indicate that 88–92% of healthcare organizations experience cyber-attacks once a year. The threats they mostly encounter are:
Ransomware attacks
These remain one of the most debilitating threats. Often initiated via phishing or exploiting unpatched vulnerabilities, ransomware encrypts critical systems and patient data, demanding a ransom. Such attacks can bring hospital operations to a standstill, directly impacting patient care and causing extensive data breaches, with recovery costs often in the millions.
Insider breaches
Not all threats originate externally. Employees or contractors with authorized access can intentionally misuse or accidentally expose patient data, from unauthorized snooping to misdirected emails. These incidents pose serious patient data security issues and are particularly challenging to detect given the authorized access.
Phishing and credential theft
Phishing remains a primary initial vector for many cyber-attacks. Highly sophisticated campaigns target healthcare providers to trick staff into revealing login credentials. Once stolen, these credentials grant attackers unauthorized access to internal networks and sensitive patient data, directly leading to data breaches.
Third-party and vendor risks
The intricate supply chain means healthcare organizations rely on numerous vendors. Insecure systems within these third parties can become direct entry points into an organization's network. A data breach at a vendor can thus compromise data for multiple partner healthcare organizations, creating a snowball effect on healthcare data security.
IoT vulnerabilities
While beneficial, the growing use of IoT medical devices introduces significant security risks. Many such devices prioritize functionality over robust security, often lacking strong authentication or encryption. This vulnerability allows potential unauthorized access to patient data or even manipulation of device functionality, impacting both healthcare data security and patient safety.
Protect your records. Preserve patient trust
Secure cloud workflows and sensitive records—tailored to your needs
Security challenges in the healthcare industry
The healthcare industry faces a unique and persistent set of challenges in maintaining effective data security in healthcare, which often exceed those found in other sectors. Successfully addressing these requires a careful understanding of the operational realities within healthcare organizations.
Balancing ease of access for medical staff with robust patient data security. Healthcare environments demand immediate, seamless access to patient information, especially in critical situations, making it a constant struggle to enforce strong network security without impeding patient care efficiency.
Integrating new technologies while maintaining compliance and security measures. The rapid adoption of innovations like AI and telemedicine requires careful integration into existing infrastructures, all while ensuring continuous regulatory compliance and maintaining a high level of data security across all systems.
Limited budgets and IT resources for advanced security tools. Many healthcare organizations, especially smaller providers, operate with constrained cybersecurity budgets and a shortage of skilled professionals, limiting their ability to invest in advanced healthcare data security tools and increasing their vulnerability to sophisticated cyber-attacks and data breaches.
Managing a diverse ecosystem of connected devices and vendor systems. A typical healthcare organization faces a challenge in ensuring consistent and effective data security across many interconnected medical devices, diverse IT systems, and numerous external vendor platforms that broaden the attack surface and increase the potential for undetected data breaches.
These challenges encourage healthcare organizations to adopt a proactive, multi-layered, and flexible approach to data protection. It's not a one-time fix but an ongoing commitment to continuous improvement, built on robust strategies and strong partnerships. Let's explore this more by diving into the best practices of data protection in healthcare.
Best practices to protect healthcare data
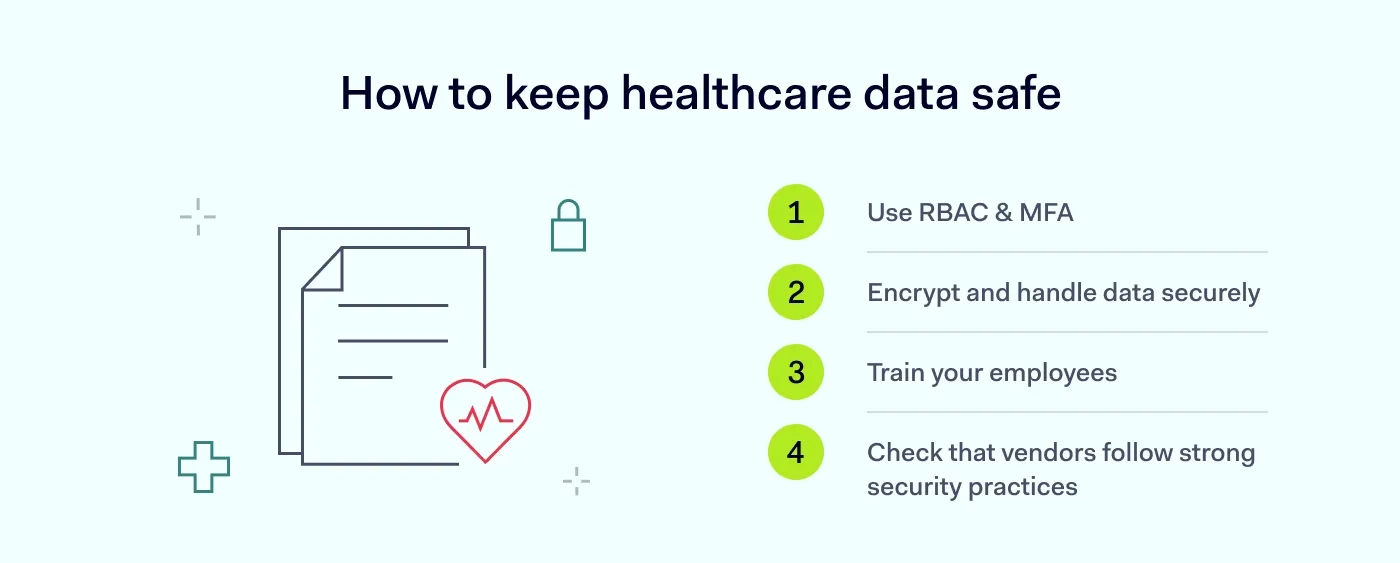
Implementing a strong healthcare data security strategy requires a combination of technology, processes, and people. These best practices are crucial for healthcare organizations aiming to prevent data breaches and maintain patient trust.
Role-based access control (RBAC) and MFA
Limit access to sensitive patient information based on job roles and enforce multi-factor authentication to add an extra layer of protection for EHRs. This ensures that employees only access the data necessary for their duties. At the same time, MFA significantly hardens login security, making it much more difficult for unauthorized users to gain access even with stolen credentials.
Encryption and secure data handling
Encrypt patient data at rest and in transit to safeguard healthcare data from unauthorized access. Even if a system is compromised, encryption renders the data unreadable to attackers. Implement secure data handling practices, including strict protocols for data disposal and secure file sharing, to minimize exposure risks.
Continuous staff training
Regularly train staff on data security practices, phishing awareness, and handling sensitive patient information securely to reduce human error. An informed workforce is often the first line of defense, capable of identifying and reporting potential threats before they escalate into data breaches.
Vendor and third-party oversight
Vet vendors and third-party services to ensure they follow strong data protection practices and do not expose your organization to unnecessary risks. Comprehensive due diligence and ongoing monitoring of third-party security postures are essential to extend your healthcare data security perimeter beyond your immediate infrastructure.
How to respond to a healthcare data breach
Despite all preventative efforts, data breaches can and do happen. A swift, organized, and compliant response is crucial to minimizing damage, restoring operational integrity, and rebuilding patient trust. This is a critical component of overall healthcare data security.
1. Contain the incident and assess the scope
Immediately isolate affected systems to prevent further damage and assess the scope of compromised patient data. Quick containment limits the spread of the breach, while a rapid assessment helps understand what data was impacted and how many individuals are affected.
2. Investigate the cause and preserve evidence
Identify how the breach occurred, preserve evidence for compliance and potential legal needs, and understand vulnerabilities in your systems. A thorough forensic investigation is vital not only for accountability but also to prevent future similar incidents and strengthen healthcare data security.
3. Notify affected parties and implement long-term fixes
Notify affected individuals and regulatory bodies as required, while addressing the root causes to strengthen data security in healthcare and prevent future incidents. Clear communication and quick action help reduce legal risks and regain trust in your data security.
How can NordLayer help with data security in healthcare
NordLayer supports healthcare providers and companies by securing their networks, helping with security compliance, and protecting healthcare data through layered security, Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA), and continuous monitoring.
Our healthcare cybersecurity solutions are designed to address the complex challenges of healthcare data security, providing a robust defense against modern cyber threats. We help healthcare organizations strengthen data security and maintain patient trust while working toward compliance with healthcare regulations.
Frequently asked questions
What types of healthcare data are most frequently targeted by attackers?
Attackers typically target electronic health records, PHI, insurance data, and payment details due to their high value on the black market. These data types are central to many data breaches in the healthcare sector.
Do smaller healthcare providers face the same security challenges as large systems?
Yes, smaller healthcare providers face similar security challenges but often with fewer resources, making them particularly vulnerable to cyber threats and data breaches. They may lack the sophisticated defenses of larger healthcare organizations.
How do you secure healthcare data?
Securing healthcare data involves a layered approach, including role-based access, encryption, continuous monitoring, regular staff training, and strong vendor management, while aligning with regulatory requirements for healthcare data protection.

Agnė Srėbaliūtė
Senior Creative Copywriter
Agne is a writer with over 15 years of experience in PR, SEO, and creative writing. With a love for playing with words and meanings, she crafts content that’s clear and distinctive. Agne balances her passion for language and tech with hiking adventures in nature—a space that recharges her.