
Anastasiya Novikava
Copywriter
Anastasiya believes cybersecurity should be easy to understand. She is particularly interested in studying nation-state cyber-attacks. Outside of work, she enjoys history, 1930s screwball comedies, and Eurodance music.
Cybersecurity

It’s impossible to eliminate every single threat, and it’s not what an effective cybersecurity risk management plan is about. In fact, it focuses on managing risks and keeping potential damage within an acceptable level. Cyber risk mitigation strategies help reduce the likelihood of incidents and limit the impact when cyberattacks happen.
This guide explains what cybersecurity risk mitigation means in practice and how to make it lead to repeatable outcomes. You’ll also get real-world examples of how cyber risks turn into security incidents and a list of best practices to reduce them.
In most attacks, hackers rely on the same core tactics: steal credentials, trick users, exploit known weaknesses, or abuse misconfigurations. They rarely come up with something exclusive or unpredictable. This is good news because it points to the first step in building a cybersecurity risk management plan: understanding the threats that show up most often in your industry and environment. Across sectors, Verizon’s 2025 breach analysis repeatedly points to ransomware, credential abuse, social engineering, and third-party exposure as common drivers of real-world breaches.
These are among the most common risks, and most companies face them regularly. It’s important to view them as business problems, because if these risks materialize, the impact won’t stay limited to technology teams.
Cyberattack consequences usually fall into a few predictable categories: money, time, trust, and legal exposure. Below are common problems organizations deal with.
According to IBM’s report, the global average cost of a data breach has exceeded $4 million annually since 2021. That’s why cyber risk mitigation requires attention across the entire organization, not just the IT budget.
So now that the main risks and their consequences are clear, the next step is to map mitigation strategies to the threats that matter most in your environment. Let’s start with the definition.
Cyber risk mitigation refers to the policies, processes, and technologies a company uses to reduce the likelihood and impact of cyber threats. It supports the broader risk management process, which helps leaders decide what to address, what to accept, and what to prepare for.
In practice, it usually means identifying critical assets, mapping likely attack paths, and choosing controls that match the business’s tolerance for downtime, fraud, and data exposure. Which controls are prioritized depends on the business: an e-commerce company may focus on checkout uptime and fraud controls, a healthcare provider on clinical system continuity and patient data protection, and a SaaS company may prioritize customer trust. A strong risk assessment guides smarter spending decisions and creates a clear record of identified risks, decisions, and owners. During audits and insurance talks, it helps prove that risks will be handled.
Although risk mitigation approaches may vary by business, most organizations don’t need a unique action plan. They can simply follow strategies already proven to work. Below are 12 practices drawn from frameworks such as the NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) 2.0, the CIS Critical Security Controls v8.1, and ISO/IEC 27001:2022 that can help establish a strong baseline.

Cyber risk mitigation starts with leadership, because they control budgets, set priorities, and assign ownership. If leadership treats cybersecurity as an IT issue instead of a business risk, key projects may stall. Enterprise risk management (ERM) solves this issue by putting cyber risk alongside financial, operational, and legal risks, with a clear cadence for executive and board oversight.
The goal in this step is simple: define governance and connect cyber risk to ERM so risk decisions happen regularly. The board (or a risk committee) approves the organization’s risk appetite and tolerance. Executives then decide how to treat each major risk: accept it, reduce it, transfer it (for example, with insurance), or avoid it. Then, they fund the controls needed to do so.
Security and IT teams provide the inputs: they assess risk exposure, track control performance, and translate technical findings into business impact (for instance, downtime and regulatory risk) so leaders can make trade-offs. This step comes first because every other control moves faster when ownership and decision rights are already clear.
The foundation for visibility is a maintained inventory of devices, software, cloud resources, and services. With that inventory as a baseline, it becomes far easier to prioritize patching, monitoring, and access controls.
Make sure that this inventory is not only accurate (“what exists”), but also useful (“what it does and why it matters”). You should also be aware of common blind spots, such as shadow IT, unknown devices, and untracked SaaS apps. Monitoring and patching usually can't cover them. You can pull data from asset management tools and a configuration management database (CMDB), but you still need a lifecycle process that keeps the inventory up-to-date when systems launch, change, and retire.
Many teams do a single annual cybersecurity risk assessment, then move on. That cadence doesn’t match today’s threat landscape, where new exposures can appear after a simple change like opening a firewall rule or adding a new SaaS integration. Treat risk assessments as a repeatable routine tied to major changes and key business systems.
Remember that a risk assessment only pays off when it leads to actionable steps that can be tracked. When you find a vulnerability, make sure to document a remediation plan that includes an owner, a due date, and a clear definition of what it means when the problem is “fixed”. Track residual risk and reassess after meaningful changes, such as a new product launch, a merger, a vendor change, or a sector-wide incident. Regular risk assessments and risk treatment belong together because “identify” without “resolve” often turns into recurring issues and repeat incidents.
With social engineering as a consistent top attack vector for years, people will likely remain a common target for hackers. That’s why regular employee training matters, and it works best when it matches real responsibilities. IT admins need different guidance than finance teams, while developers need different guidance than executives.
The main metric should focus not on attendance, but on changes in behavior. The most useful indicators are how often people report, how quickly they report, and whether they complete required policies. Verizon’s 2025 findings show phishing simulations get reported more often by users who’ve recently completed cybersecurity training, even though click rates remain high. Short refresher sessions are crucial when processes change, scams increase, or incident reviews show recurring mistakes.
Cloud services and endpoint tools come with default settings that don’t always favor security. An overly permissive cloud storage setting or a “temporary” admin exception that never gets removed can quietly create an easy entry path for attackers. To mitigate this risk, you’ll first need to define security baselines for endpoints, servers, network devices, and cloud resources (you can use vendor guidance or CIS benchmarks). Then you can make those baselines the standard for new builds and rebuilds.
Once you standardize secure configuration, you need a controlled way to approve and track exceptions and updates so the baseline doesn’t drift over time. Most configuration drift starts with small tweaks that never get reviewed again. A control process should log what was modified, who approved it, and what should happen if the change creates risk. Drift detection and automated remediation help, too, but the point is broader: configuration management works best as an ongoing control, because minor inconsistencies can turn into major openings for hackers.
Fixing every vulnerability right away isn’t realistic, so it helps to start with what attackers actually exploit. CISA’s Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) Catalog helps by listing vulnerabilities that CISA has observed as exploited in real-world attacks, which makes it a solid “patch first” signal. If a KEV item affects your internet-facing VPN or web app, it should go to the front of the queue, and if the vulnerability affects an internal system with no sensitive data, it can wait behind higher-risk targets.
Patching should be a routine you can repeat and audit:
In order for teams not to debate urgency case by case, they can use clear SLAs (service-level agreements) that define deadlines for each priority level. For example: “Patch KEV-listed vulnerabilities within 7 days on internet-facing systems,” with longer windows for lower-risk internal assets.
However, zero-day vulnerabilities need a separate, faster lane because a patch may not exist yet. In those cases, teams can apply temporary mitigations first (block or filter traffic, disable the affected feature, isolate the system, or tighten access), then install the vendor patch when it becomes available.
Identity controls often determine whether an attacker will be stopped at just one account or if they will take over the whole environment. A common best practice is to use multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all users — especially for those working remotely or having privileged accounts. Remember to protect SSO and your identity provider with the same rigor as privileged access, because attackers frequently exploit them to gain broader control quickly.
Combine strong authentication with the principle of least privilege to limit what any single account can do. Separate admin and standard accounts, run regular access reviews, and remove access promptly when roles change or employment ends. Applying least privilege in IAM limits what a compromised account can do, reducing the risk of widespread access or data breaches.
Years ago, “on the corporate network” often implied “trusted,” because most users worked from offices and most systems sat behind a firewall. Now apps and data are spread across cloud services, SaaS, remote endpoints, and third parties, with users connecting from many networks and devices.
That breaks the old “inside vs. outside” perimeter model. Zero trust addresses this by avoiding automatic location-based approval and instead verifying each request based on signals like the user’s identity, the device’s security state, and the resource sensitivity. Zero Trust treats every access attempt as potentially risky until verified, and it works best when paired with segmentation that limits lateral movement.
When you make zero-trust access decisions (for example, allowing access to an internal app only through SSO + MFA), remember that location is only one signal. A user can appear to come from an approved office IP (for example, via a corporate VPN), but if the device fails posture checks (outdated OS) or the context looks suspicious (3 AM access from an unusual device), the request should still be blocked or stepped up.
Finally, it’s important to track these signals over time because it proves risk reduction to leadership, auditors, and customers, and it helps justify what to improve next.
Attackers usually pick targets based on payoff and leverage. They look for systems that hold customer records, credentials, intellectual property, payments, or other sensitive data — systems the business can’t afford to lose. To protect them, teams should encrypt data in transit with well-configured TLS, encrypt data at rest, and secure the keys that unlock it.
Beyond preventing unauthorized access, data protection also means you can restore data after an incident. Resilience planning matters here, especially against ransomware, because attackers often try to delete or encrypt recovery copies to block restoration. Tested restores are what you can actually recover. That’s why teams run restore drills to confirm the data isn’t corrupted, access controls work, and critical systems can come back online within the timeframe the business expects.
Fast response depends on visibility. Teams need to be able to identify unusual activity, verify what occurred, and assess the effectiveness of controls. Centralized logging and ongoing monitoring help with that. For better incident response, teams need clarity on what they log (authentication events, admin actions, endpoint detections, cloud control-plane activity), where they store logs, and how long they retain them.
The challenge with monitoring is that alert noise can hide real attacks. You don’t need more alerts; what’s important is clear ownership, basic tuning, and correlation across a few key sources. For smaller organizations with limited resources, CISA’s Logging Made Easy is a no-cost tool that helps you centralize log collection and spot suspicious activity faster. With it, you can track a small set of measures, like time to detect and time to contain, and adjust monitoring as evolving cyber threats and attacker tactics shift over time. For example, when new phishing kits drive more MFA-push fatigue attempts, you can add stronger monitoring for repeated MFA prompts and unusual login patterns.
Even strong controls fail sometimes, and security incidents will happen. Microsoft’s January 2024 Midnight Blizzard disclosure—where hackers exfiltrated emails from a number of corporate mailboxes—is a reminder that even mature organizations can get hit by well-resourced threat actors. That’s why an incident response plan should be written, tested, and easy to follow under pressure. Playbooks work best when they cover likely scenarios such as ransomware, business email compromise, credential stuffing, and cloud compromise.
What will keep roles clear when pressure is real? Tabletop exercises and technical drills are a common answer. On top of that, communication steps (legal, PR, leadership), decision points (shutdowns, restores), and evidence handling should be explicit before an incident starts. Lessons learned should then feed back into incident response procedures and broader risk mitigation work, followed by another test cycle.
If a vendor processes data, holds credentials, ships code into your environment, or connects directly to your network, it can become a vulnerability. Verizon’s 2025 analysis notes third-party involvement in breaches rose sharply year over year, which is why this control belongs in any modern cyber risk mitigation plan.
Third parties often sit outside your day-to-day controls, yet they can still trigger the same operational, legal, and reputational consequences as a direct breach. Security requirements in procurement and contracts should clearly indicate notification timelines, support during incident response, and baseline control expectations. As vendor posture changes over time, periodic reassessments matter as well.
Many of the best practices above rely on tools to run at scale, especially detection, access control, configuration control, and cloud visibility. The list below focuses on categories that accelerate execution and tighten feedback loops, which help reduce cybersecurity risks as environments grow.
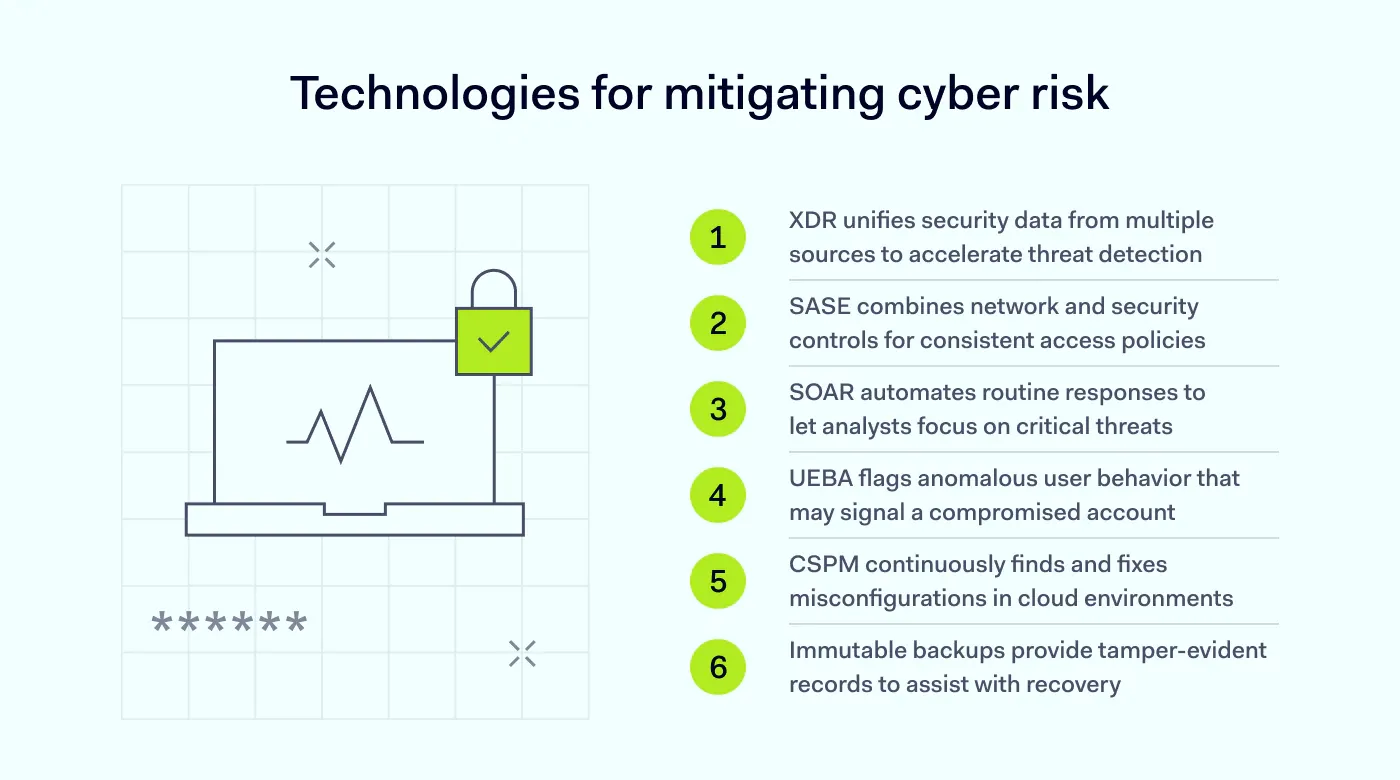
These tools help reduce the delay between “something has changed” and “someone noticed.” They cover the places where teams most often lose time, such as identity misuse, endpoint and cloud blind spots, and slow response. However, even if they help accelerate risk mitigation, they won’t replace a risk management process or fix ownership gaps.
Strong cyber risk mitigation relies on consistency: access rules that don’t drift, visibility that doesn’t leave gaps, and workflows that work under pressure. The right tools can reduce manual effort for IT and security teams while keeping policies enforceable across users, devices, and apps.
Nord Security’s business products support different parts of a cybersecurity risk management plan:
Together, these products can support risk management strategies across prevention, detection, and response. However, tools alone won’t fix outdated software, replace employee training, or run an incident exercise for you. Outcomes still depend on clear policies, configuration, and continuous monitoring.
Contact sales to see how Nord Security can support your risk management plan.
Subscribe to our blog updates for in-depth perspectives on cybersecurity.