Summary: Learn about Zero Trust Data Protection and its role in modern cybersecurity. See how it redefines data control, access, and risk in high-threat environments.
Today, traditional perimeter-based security models are no longer enough. With sensitive data flowing across hybrid environments, remote endpoints, and decentralized cloud systems, the challenge is no longer where data is—but who can access it and under what conditions. Zero Trust Data Protection offers a modern, policy-driven framework that rethinks how data security should function in a world where implicit trust is a liability.
This article explores what Zero Trust Data Protection really means, how it differs from broader Zero Trust security strategies, and why forward-thinking enterprises are adopting it as a foundational layer of their cybersecurity. If your organization handles sensitive data—and needs to ensure it's always protected regardless of location, user, or device—this guide is for you.
What is Zero Trust Data Protection?
Zero Trust Data Protection (ZTDP) is an advanced security approach that applies Zero Trust principles specifically to how data is accessed, used, and protected. Unlike traditional models that assume trust based on network location or credentials, ZTDP follows the “never trust, always verify” philosophy—enforcing strict access controls and continuous validation across every layer of data interaction.
While it shares DNA with Zero Trust architecture, ZTDP goes a step further by shifting the focus from infrastructure to data access itself. This means that even if a user, device, or application gains entry into a trusted environment, data access is never assumed. Instead, policies built around least privilege access, real-time context, and behavioral signals govern who or what can interact with sensitive information—and under what conditions.
Go beyond "never trust, always verify"
Redefine your defense with cutting-edge Zero Trust segmentation. Get your free PDF.
How does Zero Trust differ from traditional data security models?
Traditional data security models were built around the idea of a secure perimeter—think firewalls, VPNs, and on-premises access controls. In these models, once a user or device was authenticated and “inside the network,” they were typically granted broad access to internal systems and protected data. Trust was implicit, and security was largely dependent on defending the perimeter.
Zero Trust Data Protection completely upends this approach. Rooted in Zero Trust principles and enforced through Zero Trust architecture, ZTDP assumes that no user, device, or process should be trusted by default—even if inside the corporate network. Instead, every attempt to access data is treated as potentially hostile and evaluated in real time using contextual signals like identity, device health, geolocation, and behavior.
Another key distinction is how access is granted. While legacy systems often rely on static role-based access, ZTDP enforces least privilege access, ensuring that users can only access the data and resources they absolutely need, and only for the duration required. These strict access controls dramatically reduce the attack surface and limit lateral movement in the event of a breach.
In short, while traditional models focus on protecting the network, Zero Trust Data Protection is designed to protect the data itself—wherever it resides. This shift is critical in remote work, cloud adoption, and escalating insider threats. For organizations aiming to modernize their security posture and prevent unauthorized access or data loss, ZTDP isn’t just an upgrade—it’s a necessity.
What’s the difference between Zero Trust Data Protection and Zero Trust Data Security?
While often used interchangeably, Zero Trust Data Protection and Zero Trust Data Security serve distinct purposes—and understanding the difference is critical for businesses building advanced cybersecurity strategies.
In short, ZTDP differs from Zero Trust Data Security in that it centers more narrowly on data as the protected asset, rather than the broader ecosystem of users, networks, and endpoints. It strengthens an organization’s security posture, mitigates the risk of unauthorized access, and forms the backbone of effective data loss prevention strategies in modern, decentralized environments.
To put things into perspective, Zero Trust Data Security refers to the broader application of the Zero Trust security model. It includes securing networks, applications, endpoints, and identities, and is designed to eliminate implicit trust across the IT environment. Its goal is to reduce attack surfaces and prevent lateral movement through continuous verification and contextual authentication.
Zero Trust Data Protection, on the other hand, applies those principles directly to confidential data itself. Rather than focusing on infrastructure or identity per se, ZTDP enforces least privilege access to data at the object level—governing who or what can interact with specific data assets, under which conditions, and for how long. This data-centric approach is especially valuable in complex, distributed environments where access to data is fluid and dynamic.
The distinction matters. A company may implement Zero Trust security controls across its network and endpoints, but still leave data vulnerable if access policies aren't enforced at the data layer. ZTDP closes that gap, enabling granular enforcement, contextual visibility, and stronger protection against unauthorized access—whether from external actors or insider threats.
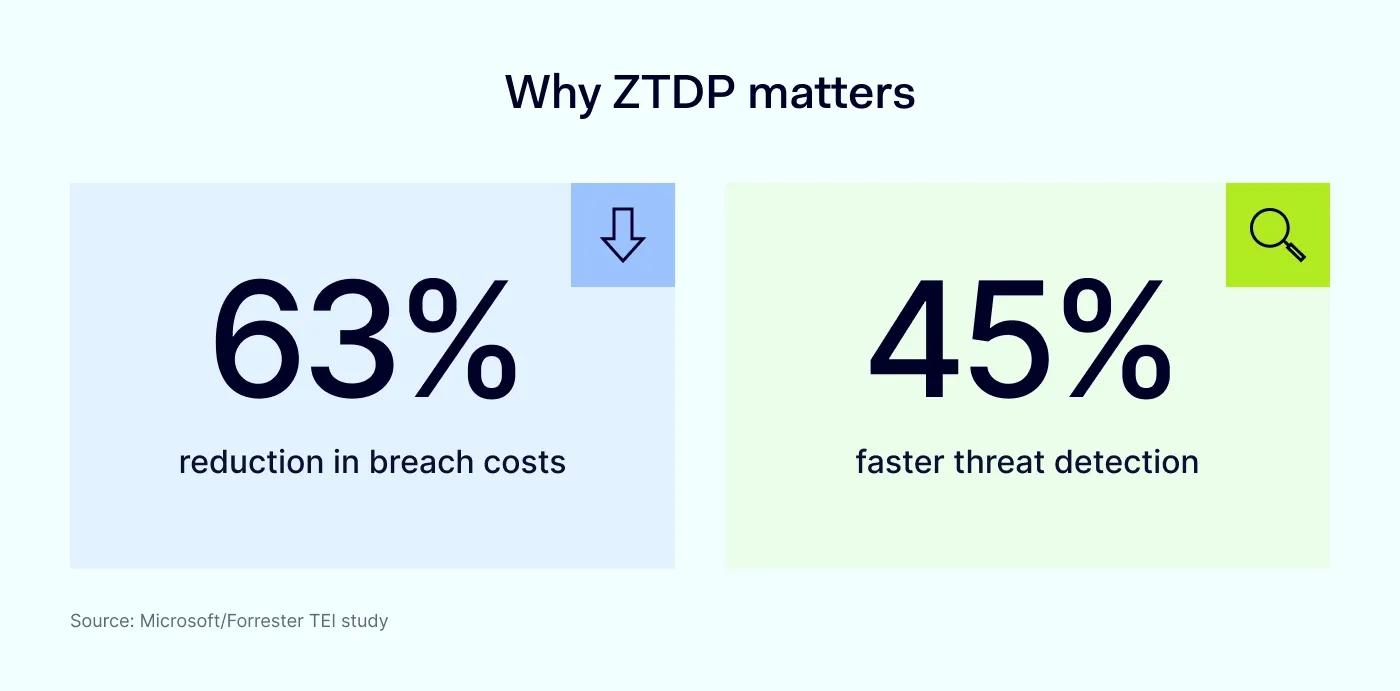
This difference isn’t just theoretical. A 2021 study found that organizations implementing mature Zero Trust strategies—including data-level enforcement—experienced 63% lower breach costs and detected incidents 45% faster than those relying on traditional models or partial Zero Trust rollouts. In another example, a mid-sized healthcare provider reduced insider threat incidents by 40% after adopting data-centric Zero Trust controls, which limited data access to authorized personnel only, in real-time conditions.
For B2B organizations handling regulated or high-value data, Zero Trust Data Protection represents the next level of strategic investment—one that directly supports compliance, operational resilience, and long-term risk reduction.
Benefits of Zero Trust Data Protection
Securing data today isn’t just about keeping intruders out—it’s about controlling exactly who can access what, and under what conditions. As businesses grow more distributed and data becomes increasingly portable, traditional security approaches that focus on the perimeter or user identity alone are no longer enough. Zero Trust Data Protection takes a different approach: it puts the data at the center of the security strategy.
Below are some of the most valuable outcomes organizations can expect when implementing a ZTDP model:
Minimizes the attack surface
ZTDP reduces risk by enforcing least privilege access—only verified users and systems get access to the data they’re explicitly authorized to use. This limits the impact of compromised credentials or insider threats and prevents lateral movement within the environment.
Improves data visibility and control
One of the core benefits of Zero Trust—and of ZTDP specifically—is enhanced operational visibility. This makes it easier to detect unusual activity, apply dynamic policies, and respond to incidents faster.
Supports regulatory compliance
ZTDP helps meet regulatory requirements by applying precise, auditable controls to protected data. Organizations can enforce consistent policies and demonstrate that access is both justified and logged, simplifying audits and reducing compliance risk.
Key principles of Zero Trust applied to data protection
The principles of Zero Trust security form the foundation of an effective data protection strategy. When applied specifically to securing sensitive data, these principles help organizations reduce risk, enforce precise access controls, and respond dynamically to changing threats. Here are the core Zero Trust security principles as they relate to data protection:
Never trust, always verify. Trust is never assumed—even within the corporate network. Every request to access data must be authenticated, authorized, and continuously evaluated based on context such as user identity, device health, and location.
Least privilege access. Users, applications, and devices are granted only the minimum level of data access necessary to perform their function. This reduces the blast radius of potential breaches and enforces tight control over who can interact with which data.
Continuous verification. ZTDP relies on ongoing validation—not one-time authentication. Access is reassessed in real time using telemetry and behavior analysis, ensuring that session context and trust levels remain valid throughout.
Related articles

Agnė SrėbaliūtėAug 7, 202415 min read

Joanna KrysińskaOct 31, 20249 min read
How NordLayer helps implement Zero Trust Data Protection
Implementing Zero Trust Data Protection requires more than just high-level strategy—it demands technology that can enforce granular access controls, support dynamic work environments, and scale securely across your infrastructure. That’s where NordLayer’s platform stands out.
NordLayer enables organizations to apply Zero Trust security principles directly to data access, ensuring that every interaction with sensitive resources is authorized, authenticated, and context-aware. With identity-based Network Access Control (NAC), network segmentation, and Device Posture Security, NordLayer helps enforce least privilege access across your distributed workforce.
Its centralized Control Panel allows IT teams to manage user permissions, apply policy changes in real time, and monitor data activity across cloud and on-prem environments. By continuously verifying user and device trust levels, NordLayer ensures that access is both dynamic and compliant with modern security standards.
For organizations navigating complex compliance landscapes or hybrid infrastructure, NordLayer offers the tools to move from legacy perimeter-based models toward practical, enforceable Zero Trust solutions—ones that place data access at the core of the security strategy.

Aistė Medinė
Editor and Copywriter
An editor and writer who’s into way too many hobbies – cooking elaborate meals, watching old movies, and occasionally splattering paint on a canvas. Aistė's drawn to the creative side of cybercrime, especially the weirdly clever tricks scammers use to fool people. If it involves storytelling, mischief, or a bit of mystery, she’s probably interested.