Summary: In 2026, cloud security shifts from reaction to prevention. AI defense and geopatriation redefine cloud environments where identity-first and autonomous strategies ensure business security.
For years, moving to the cloud was sold as a great escape from the clunky fragility of on-site servers. But in 2026, that perception is changing. While companies have migrated to the cloud at lightspeed, their security is still stuck in the slow lane. The arrival of AI and millions of IoT devices hasn't just opened more doors for attackers—it has handed them the keys.
The old way of "patching holes" after a breach is no longer viable. To survive today, businesses must stop reacting and start preventing. The following cloud security trends in 2026 aren’t just strategies—they are the first step toward keeping your business in one piece.
Key takeaways
Zero Trust becomes the default model for cloud environments. Identity-first controls matter more than perimeter defenses.
Cloud misconfigurations still cause many incidents. Open storage and unpatched public assets remain common risks.
Cloud-native security and DevSecOps merge into one workflow. Cloud service providers embed security into their platforms, which can increase threat visibility by 40%.
Data location becomes a security decision. The geopatriation trend pushes sensitive workloads toward sovereign or local environments.
AI moves from alert overload to early detection. Use it to spot anomalies, reduce false positives, and speed response time.
Quantum-safe encryption starts now. Plan a post-quantum cryptography (PQC) roadmap before “harvest now, decrypt later” becomes real damage.
Compliance frameworks tighten and multiply. Treat data mapping, retention, and deletion proof as ongoing work, not a one-time checkbox.
The state of cloud security in 2025
Now, it is almost impossible to run a modem business without the cloud. According to the Cloud Security Alliance, 98% of organizations globally rely on cloud services. But while adoption of cloud services is universal, securing cloud environments has become a massive challenge for IT teams—and for good reason: 82% of data breaches now involve the cloud.
What's interesting is that the biggest cloud security threats in 2025 were surprisingly basic. It wasn't always hackers breaking in; it was them exploiting vulnerabilities left behind by organizations. In 2024, 21% of companies had at least one storage bucket that was effectively active and open to the public, exposing sensitive data to anyone who knew where to look. Additionally, 81% of organizations had "neglected assets"—public-facing systems running outdated software or left unpatched for months.
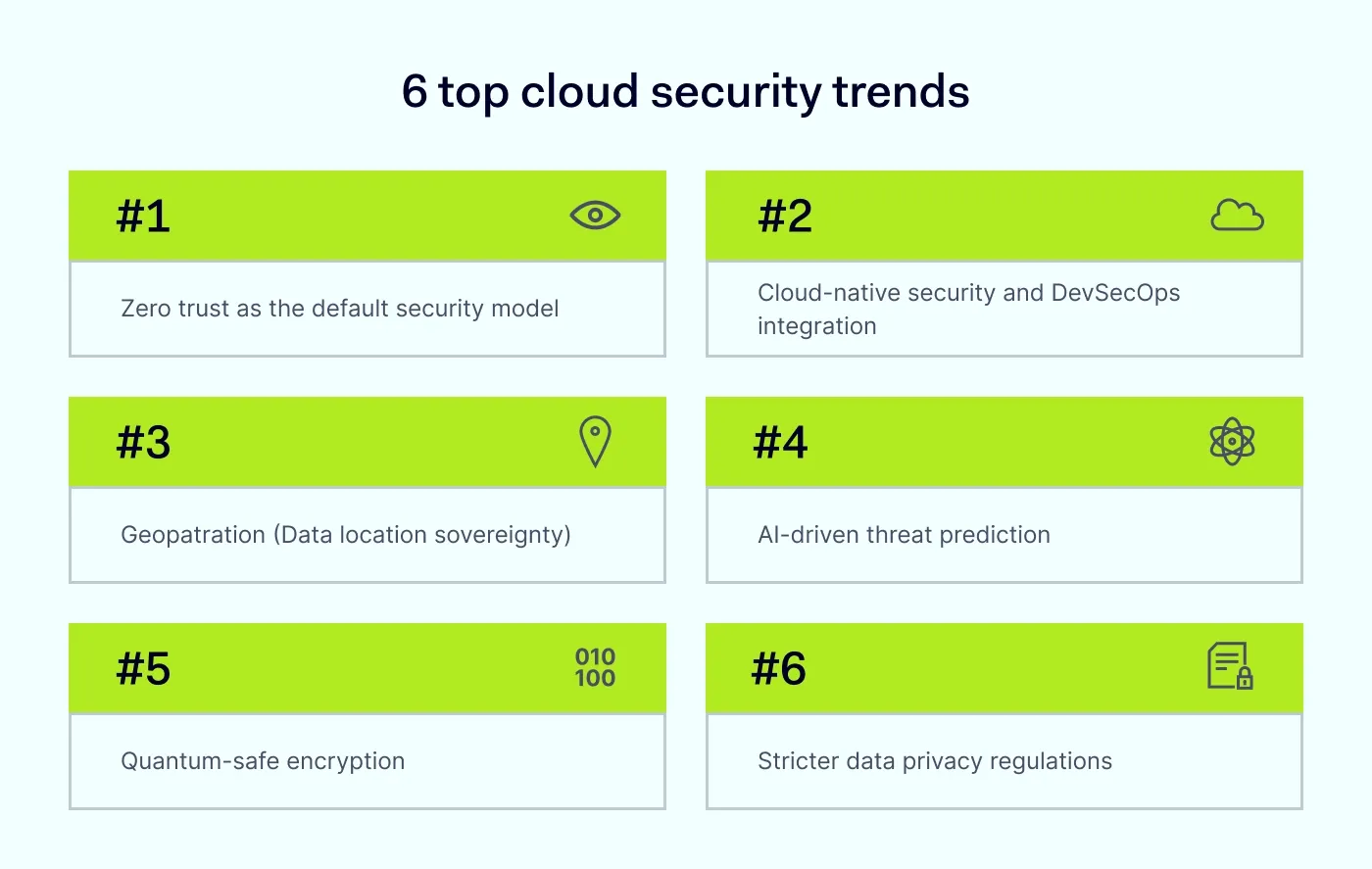
6 biggest cloud security trends in 2026
In 2026, the cloud is no longer just a place to store data; it is the arena where the future of corporate survival is being contested. According to Gartner, this year, cybersecurity will no longer be just a technical problem but a geopolitical and operational necessity. Here are the six cloud security trends defining this year.
Trend 1: Zero trust as the default security model
One of the biggest cloud security trends is that zero trust has become the industry standard. This model relies on the “trust no one, verify everyone at every step” rule, treating every login as a potential breach.
This state of constant vigilance is the only reliable defense against modern threats like ransomware and identity theft. Forrester’s Technology and Security Guide predicts that 2026 is the year identity-first security becomes the primary battleground, especially as machine identities now outnumber human employees by 82 to 1.
Trend 2: the consolidation of cloud-native and DevSecOps
The days of "grafting" security onto the cloud are over. The market has shifted toward cloud-native protection platforms (CNAPPs) that integrate directly with cloud providers like AWS and Google Cloud. By embedding security into the code itself—the "DevSecOps" approach—businesses ensure their infrastructure is secure by design. As Gartner notes, organizations that successfully adopt this model will gain 40% greater visibility into their threat surface.
Trend 3: geopatriation (or why data security is driving its location)
For years, companies treated the cloud like a giant, borderless warehouse. But in 2026, they are realizing that where your data lives is just as important as how it is protected. This shift—called geopatriation—is the strategic move to relocate sensitive data out of global clouds and into “sovereign” environments: local providers or a company’s own data center.
The scale of this trend is immense. Gartner predicts that by 2030, 75% of enterprises in Europe and the Middle East will have moved their critical workloads back to local solutions—a massive jump from just 5% last year.
Related articles

Anastasiya NovikavaOct 16, 202516 min read

Maciej SikoraOct 15, 20257 min read
Trend 4: AI for predictive threat detection and response
In the sprawling complexity of the cloud, manual monitoring is no longer feasible; only AI can analyze the volume of data needed to establish a behavioral baseline and spot anomalies in real time.
This shifts security from reactive to predictive. Instead of waiting for a breach to trigger an alert, algorithms identify suspicious deviations before they escalate. By filtering out false positives and prioritizing vulnerabilities based on real-world risk, AI allows IT teams to improve their cloud security posture.
Trend 5: quantum-safe encryption
The "harvest now, decrypt later" threat has moved from theory to boardroom anxiety. Cybercriminals have spent years stealing encrypted data with the hope of breaking it once quantum computers mature. That moment has arrived. In 2026, the financial and healthcare sectors are leading the migration to post-quantum cryptography (PQC). Many companies from other sectors have already made 2026 the critical year for replacing classic RSA algorithms with lattice-based protocols.
Trend 6: emphasis on improved data privacy regulations
Regulatory compliance is now a top priority for cloud security managers. The sheer volume of regulations is exploding, creating a complex environment for IT teams. While the European Union relies on a single law (GDPR), the United States is passing a confusing array of state laws, from California’s CCPA to Montana’s Consumer Privacy Act. Another challenge is that "data subjects" now have the right to be forgotten. However, the cloud’s ability to easily replicate and copy data makes it difficult to prove that every single copy of a record has been deleted.
Stay ready for what’s next in cyber
Secure your business with toggle-ready protection
Key challenges in cloud security in 2026
As many as 82% of breaches happen in the cloud. Understanding which cloud security challenges your business can face is key to protecting it.
Identity and access management (IAM) flaws. Identity is now the cloud’s most watched—and weakest—link. Issues with IAM tools may allow attackers to access your network systems and compromise your critical data.
Fighting threats instead of preventing them. Many organizations still measure failure rather than prevent it. By focusing on surface-level stats like incident frequency or multi-factor authentication (MFA) enrollment, they track mere compliance. This is reactive, not protective. True resilience is missing because metrics don't yet measure actual risk reduction.
The multi-cloud complexity gap. As architectures sprawl, human error scales with them. A single misconfiguration or an overly broad permission set can accidentally expose an entire database. In a multi-cloud world, "simple" mistakes now have global consequences.
The regulatory struggle. Storing sensitive data in the cloud is high-stakes now. Meeting strict compliance standards like
GDPR or
HIPAA is no longer a checklist exercise, but a constant struggle against liability.
Inconsistent visibility into cloud workloads. With assets spread across hybrid clouds and SaaS apps, user activity and data may remain hidden without continuous monitoring tools. This makes it more challenging for IT teams to detect anomalies or even breaches.
How can NordLayer help?
NordLayer provides cloud security solutions directly addressing 2026’s core challenges:
Neutralizing multi-cloud complexity. NordLayer integrates into secure access service edge (SASE) and security service edge (SSE) architectures, offering a unified view to enforce centralized policies across AWS, Google Cloud, and on-premises servers.
Preventing data exfiltration. Our
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) tools identify and monitor sensitive data, while NordLayer helps control its access and transfer.
Solving the identity weak link.
Identity and access management (IAM) tools can help your organization define
who can access
which resources and manage user identities. IAM is an important part of zero-trust architecture.
Enterprise-grade business protection.
NordLayer’s cloud security solutions help reduce risks, simplify operations, and protect cloud environments by combining secure access, greater visibility, and control.
Controlling sensitive data at the point of use.
NordLayer Browser helps minimize the risk of accidental information leaks from endpoints. By enabling session-level controls, the business browser restricts actions such as copy and paste, file uploads or downloads, screen sharing, and the use of external devices.
Cloud security is not a single tool, but a multi-layered strategy. By deploying NordLayer, you can build a resilient defense that scales seamlessly with your cloud adoption.
FAQ
Why is cloud security more important than ever?
As businesses increasingly rely on the cloud for scalability, cost efficiency, and flexibility, security risks also rise. A robust cloud security strategy is crucial for protecting data, preventing breaches, and complying with more stringent regulations.
How will quantum computing impact cloud security?
Quantum computing is revolutionizing cloud computing by solving complex problems that traditional systems can’t, introducing new opportunities and challenges for cloud security. It requires new approaches to encryption and data protection.
What is the future of AI in cloud security?
In 2026, predictive LLM-driven hunting and automated compliance will replace manual oversight, turning security into a proactive business enabler. Ultimately, the cloud will become a permanent "arms race" between competing algorithms—where the fastest learner wins.
How to improve cloud computing security?
To improve cloud security, adopt a zero-trust architecture. Strengthening your defense requires enforcing strict multi-factor authentication (MFA), encrypting all data at rest and in transit, and maintaining automated, immutable backups.
Success also depends on mastering the shared responsibility model, in which you secure everything in the cloud while the provider secures the underlying infrastructure. Finally, replace manual oversight with continuous monitoring and automated response to catch misconfigurations and human errors before they turn into breaches.
What challenges will businesses face with multi-cloud environments?
Multi-cloud can bring operational chaos due to fragmented visibility. Companies face a dangerous security gap where inconsistent policies across providers lead to misconfigurations—the cause of 99% of cloud failures.
Financially, unpredictable egress fees can consume 45% of project budgets, while a severe talent shortage makes finding experts who speak "multi-cloud" increasingly difficult.
How can AI improve cloud security in 2026?
AI will play an important role in cloud security by automating threat detection and response, predicting resource needs, and enhancing performance. AI-powered systems will allow businesses to anticipate and neutralize threats before they become serious issues.
What challenges will businesses face with multi-cloud environments?
Managing security across multiple cloud platforms will become even more complex in 2026. AI and machine learning will help scale defenses and provide faster, smarter decision-making to combat risks in multi-cloud setups.
What are the key security risks for businesses using cloud infrastructure?
Key threats include widespread misconfigurations—such as open storage buckets—and "neglected assets" left unpatched. Also, identity management remains the critical weak link, while multi-cloud complexity creates visibility gaps where human error can accidentally expose data to regulatory liability.

Joanna Krysińska
Senior Copywriter
Joanna's family has a history in math and engineering, and she has dedicated her life to simplifying complicated technical ideas. She helps people understand how hackers think and how to stay ahead of them by concentrating on the human side of cybersecurity.