Summary: This article explores the critical areas shaping 2026 cybersecurity spending. Find out how businesses balance AI-based threats, cloud expansion, and the rising cost of security talent.
Cybersecurity budgeting for 2026 is defined by agility. With more geopolitical tensions and technology evolving at dizzying speed, your financial plan needs to adapt as quickly as the threats you face.
One of the biggest challenges this year is the dual nature of AI. While 77% of companies use it to detect suspicious network behavior, AI-specific vulnerabilities are now one of the fastest-growing cyber risks. Your 2026 budget should bridge that gap, investing in efficiency and automation while covering the added costs of securing AI systems.
Security investment in security is also growing worldwide. While global IT spending will exceed $6.08 trillion this year, the real story is security software, which now eats up about 40% of the average cybersecurity budget.
This article helps you understand key factors influencing your security spend and provides a roadmap for smarter allocation.
Key takeaways
AI can speed up detection and response, but it also introduces new risks, so your budget should cover both AI adoption and AI security.
Geopolitical conflicts are fueling cyberattacks, so planning should assume you’ll be targeted—not treat it as a remote possibility.
Cloud budgets are shifting from migration to efficiency, with more spend going to performance and cost control under AI-driven compute demands.
Company size shapes the approach, with large enterprises often building in-house teams while smaller businesses lean on managed security service providers (MSSPs).
Security software is now taking a larger share of budgets, driven by growing spend on cloud-native tools and automation.
Regulations like the EU’s Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) and NIS2 are increasing security spend to reduce outage risk and avoid penalties.
2026 cybersecurity budget outlook
As geopolitics drives more cyberattacks, the cost of effective defense is rising. According to Gartner, security spending will hit $213 billion in 2026 (a 12.5% jump from last year), caused largely by the shift to cloud-based software, generative AI, and advanced automation.
As companies move away from legacy on-premises hardware, they are pouring money into security software—especially cloud security posture management (CSPM) and solutions with built-in security controls. Organizations are spending more because the security tools they use are getting more complex, and both defenders and threat actors are using AI to sharpen their tactics.
What factors influence cybersecurity budgets
To build a resilient cybersecurity budget for 2026, organizations are shifting from reactive spending to strategic resource allocation. Let’s explore what influences this year’s security spending.
Geopolitical volatility
Geopolitical factors are reshaping cyber risk mitigation strategies. As state-sponsored groups become more capable, budgets are shifting toward national-level resilience.
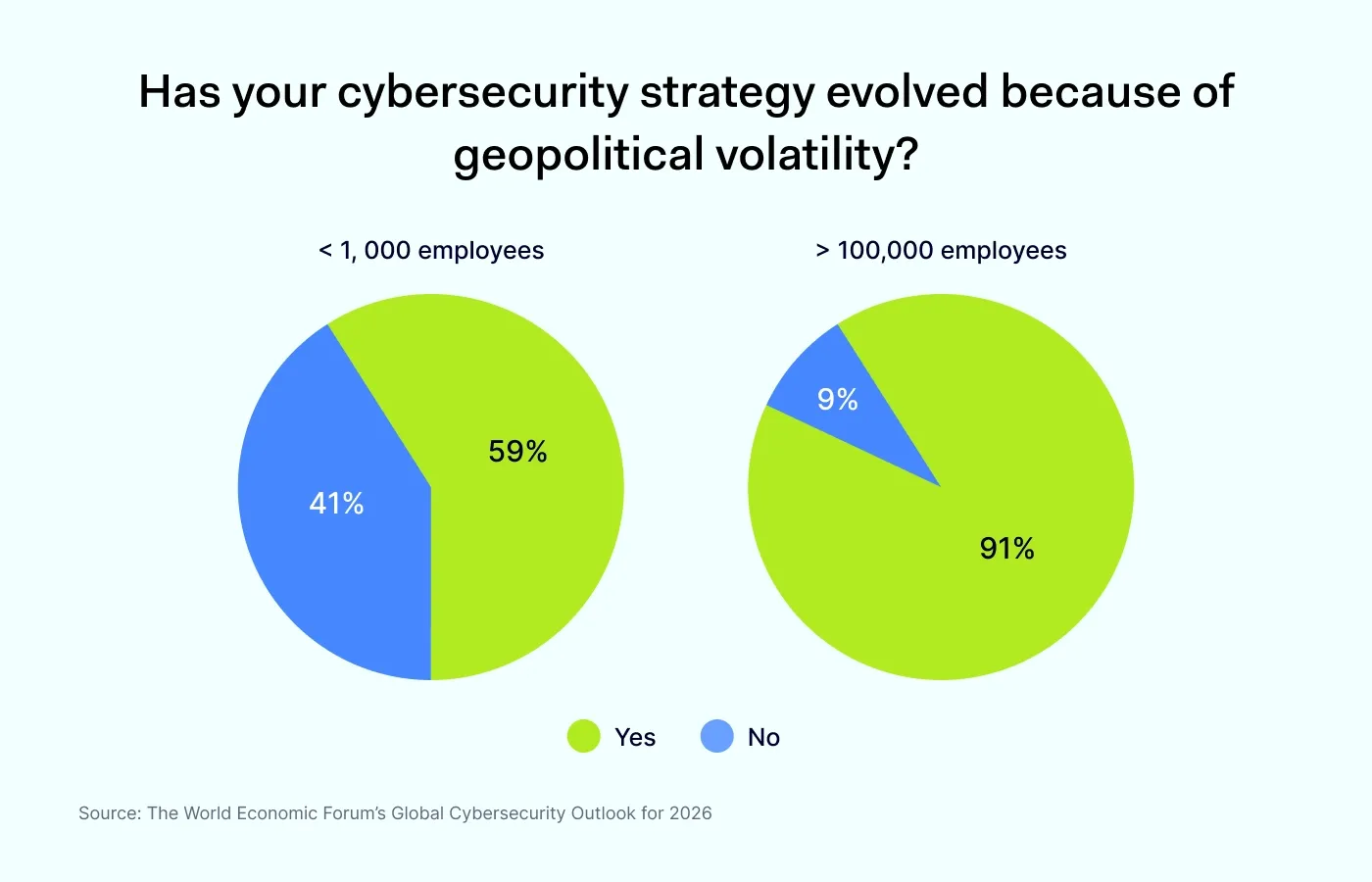
Strategic adaptation. According to the World Economic Forum’s Global Cybersecurity Outlook for 2026, 91% of large organizations have adjusted their cybersecurity strategies due to geopolitical volatility.
Proactive planning. 64% of organizations now explicitly include geopolitically motivated cyberattacks in their formal risk strategies, moving from "if" to "when" scenarios.
Security and AI
In 2026, global AI spending is projected to exceed $2 trillion as organizations move beyond experiments to production use. However, this rapid adoption has created new risks. As many as 87% of organizations experienced an AI-based attack last year—a 72% jump—making several budget lines hard to avoid:
AI governance. To support massive data and compute needs,
84.1% of total AI spend is now concentrated in high-performance computing and servers.
Identity threat detection and response (ITDR). As deepfakes and credential stuffing become standard tactics for attackers, ITDR has moved from a "nice-to-have" to a critical budget line.
Workflow integration. Spending is moving toward embedding AI into daily workflows and automation to speed up decision-making.
Compliance
Stricter compliance requirements, such as the EU’s DORA and NIS 2, are also pushing organizations to invest more in their security posture to reduce the risk of outages and penalties. This involves:
Cloud and app security. Protecting cloud workloads, application programming interfaces (APIs), and non-human identities.
Data security and visibility. Implementing tools to monitor sensitive data across hybrid and AI-enabled environments.
Uptime investments. Allocating funds for backup and disaster recovery to meet tougher "uptime" expectations.
Strong security, smart spending
Invest where it counts without compromising your defenses
The cloud budget shift: efficiency over migration
In 2026, cloud spending is less about moving to the cloud and more about running it efficiently. Because AI requires massive compute power, many companies are seeing their cloud costs surge. The goal now is cloud-native analytics—placing security tools closer to where data is generated and stored, so teams can detect threats faster.
Planning cybersecurity budget allocation for 2026
As we all know, every company faces a different set of challenges. Your risks depend on factors like your company size, industry, and infrastructure—so it makes sense that your budget should be built to match those specific needs.
Your company size
A global corporation and a local business face many of the same threats, but they need different defenses. Large enterprises typically have larger attack surfaces—more employees, more cloud apps, and more locations—so they often invest in in-house security teams and 24/7 security operations centers (SOCs).
| | |
|---|
| Protecting complex infrastructure | In-house teams and 24/7 SOCs |
| Mitigating immediate threats | Outsourced experts (MSSPs) and cloud tools |
Smaller businesses, on the other hand, should focus on being lean and effective. Rather than building large in-house teams, many small and mid-sized businesses (SMBs) rely on managed security services providers (MSSPs).
Your industry
Not all industries invest the same amount in security. Funds allocation varies based on risk exposure, regulatory requirements, and operational complexity.
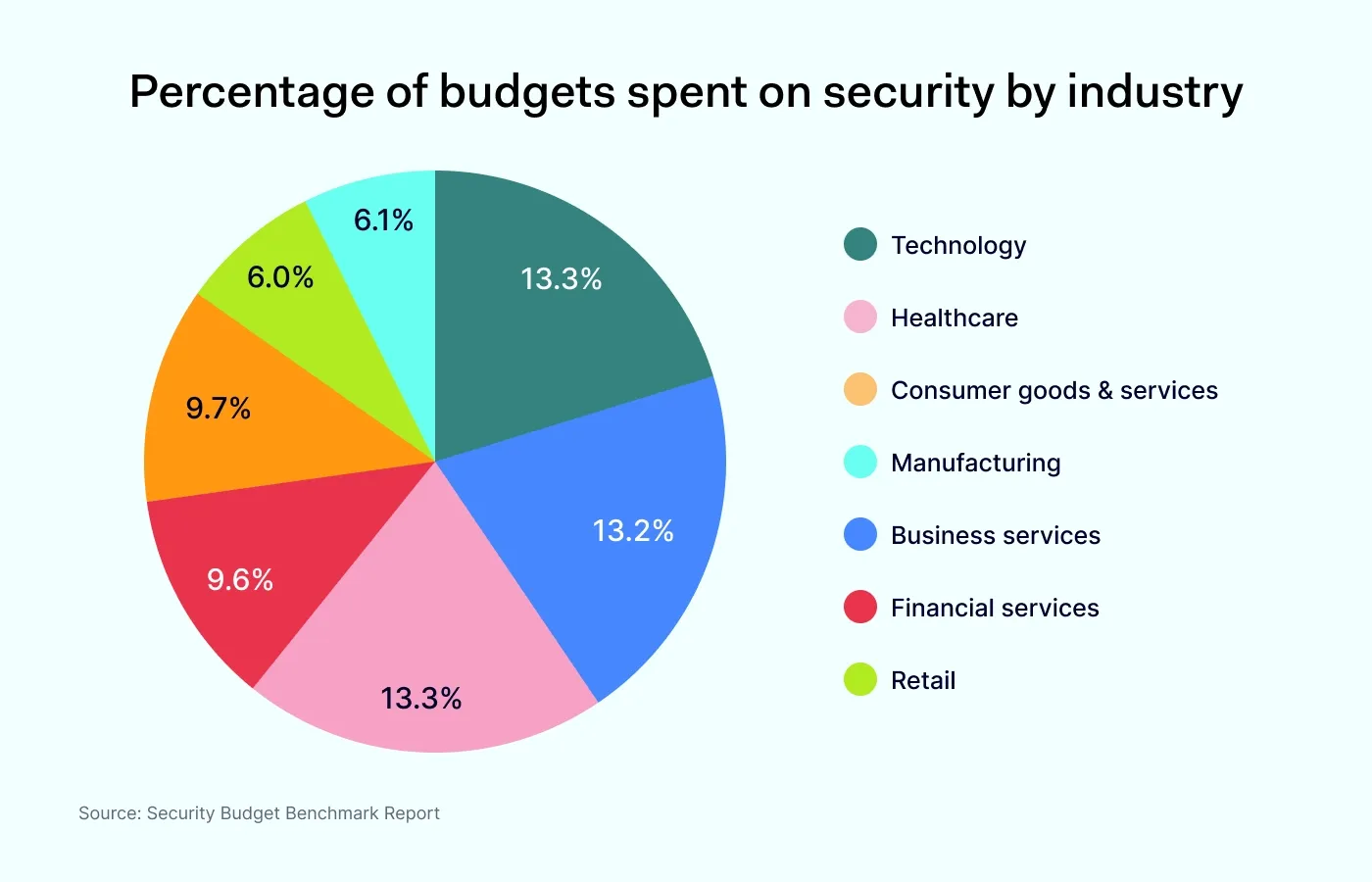
Here's how cybersecurity spending breaks down across key industries:
Technology, healthcare, and business services tend to spend the most on security, allocating over 13% of their IT budgets, mainly because of high data sensitivity and strict compliance requirements.
Financial services, despite heavy regulation, allocate slightly less (9.6%), likely due to a mature, optimized security infrastructure.
Manufacturing and retail invest the least, though supply chains and e-commerce threats are pushing these numbers upward.
The bottom line is that you should customize your spending to meet the specific industry regulations and protect your company from threats in your field.
Related articles

Agnė SrėbaliūtėJan 20, 20268 min read

Joanna KrysińskaJan 15, 20269 min read
A practical breakdown of your security budget: tools, staff, and services
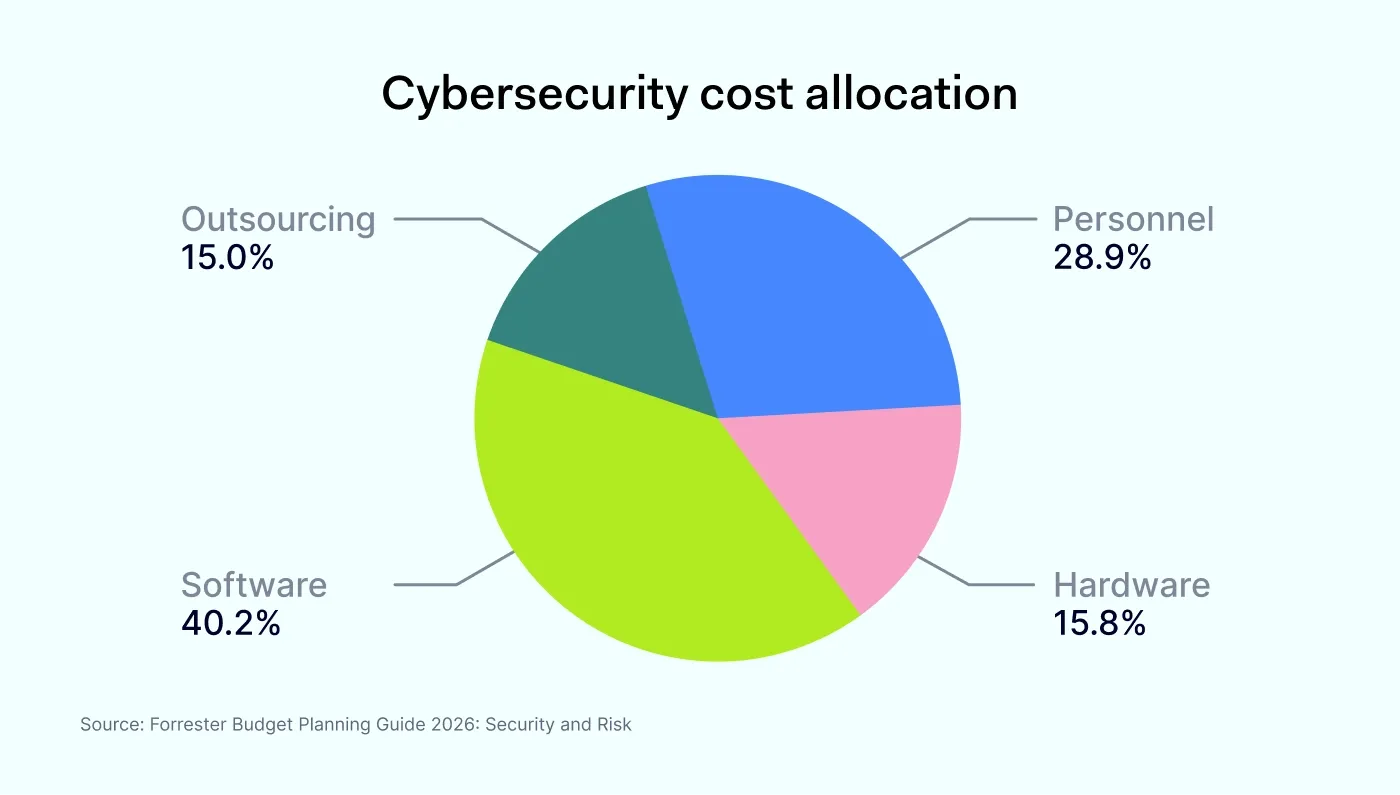
A balanced cybersecurity budget requires a strategic split between software, outsourcing, hardware, and personnel. Let’s look in more detail at how 2026 budgets break down.
Security tools
Investing in tools that detect, block, and monitor cyber threats is key to a modern business strategy. To build a resilient defense, organizations should prioritize spending on firewalls, web application firewalls (WAFs), endpoint detection and response (EDR), and cloud security solutions. AI and machine learning (ML) are also more important.
How much an organization spends on technology depends on its size. This is how cybersecurity budget allocation on technology looks by business size:
Small businesses: 15–30% of the total cybersecurity budget
Medium-sized businesses: 30–50%
Large enterprises: 40–60%
Managed security services
Organizations that lack the resources for full-time, in-house security operations often rely on MSSPs. They provide 24/7 monitoring and threat intelligence, which can be more cost-effective than hiring specialists internally.
This is how budget allocation on MSSPs looks by business size:
Small businesses lead with 20–40% of their total cybersecurity budget.
Medium-sized businesses allocate 10–30% of their budgets to supplement their teams.
Large enterprises spend only 5–15% of their total cybersecurity budget on MSSPs because of their internal capabilities.
Staff
Hiring and retaining talent is one of the biggest hurdles in cybersecurity today, largely because there simply aren’t enough professionals to go around. This skills gap makes staffing a key item of any security budget, though the costs vary by company size.
Small businesses usually spend about 10–20% of their budget on outside consultants, while medium-sized companies often put 20–40% toward hiring and training their own teams. Large corporations go even further, frequently dedicating up to half of their entire cybersecurity budget just to cover the high salaries and ongoing management needed to keep a top-tier team in place.
| Budget allocated to personnel |
|---|
| |
| |
| |
Planning your 2026 security spend: sample budget splits
To plan your 2026 budget, balance your spending between modern tools (like AI and cloud security) and the professionals needed to manage them.
Budget benchmarks by company size:
Small businesses allocate 4–10% of the total IT budget to security. Most of this goes toward external consultants and basic protection tools.
Medium-sized businesses dedicate 8–15% of the IT budget to building internal teams and adopting automated detection tools.
Large enterprises spend 10–20% of the IT budget on advanced AI-based technology and senior internal talent management.
The real cost of not investing in cybersecurity
Investing in cybersecurity is no longer just an IT expense, but a vital element of business protection strategy. If you don't treat security as a priority, the fallout can be devastating. A single breach triggers a chain reaction of damage. Beyond the immediate loss of revenue and the massive cost of recovering systems, the reputational damage can be permanent.
In regulated industries such as finance, healthcare, and public administration, meeting security requirements is also a legal obligation. Falling short can lead to costly lawsuits, penalties, and increased government oversight. Ultimately, cyber spending should not be treated as a cost center, but as a strategic investment in security.
How can NordLayer help with your 2026 security budget?
With more AI-based cyberattacks, cybersecurity remains a priority. Organizations need security that’s effective and predictable in cost.
NordLayer can be a cost-effective option for businesses of all sizes. Here’s why:
Flexible and scalable. You can easily add or remove licenses as your team grows or changes. Start with a basic plan and upgrade or downgrade anytime. You only pay for what you need.
Lower costs with cloud-based delivery. NordLayer is cloud-based, so there’s no need for expensive hardware or maintenance. It’s quick to set up, easy to manage, and saves time and money.
NordLayer helps you strengthen security without overspending. Contact us today to discuss a setup that fits your 2026 budget.

Joanna Krysińska
Senior Copywriter
Joanna's family has a history in math and engineering, and she has dedicated her life to simplifying complicated technical ideas. She helps people understand how hackers think and how to stay ahead of them by concentrating on the human side of cybersecurity.