Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) is the practice of employees using their personal devices for work. It’s become popular because every working-age adult today owns a smartphone and a laptop.
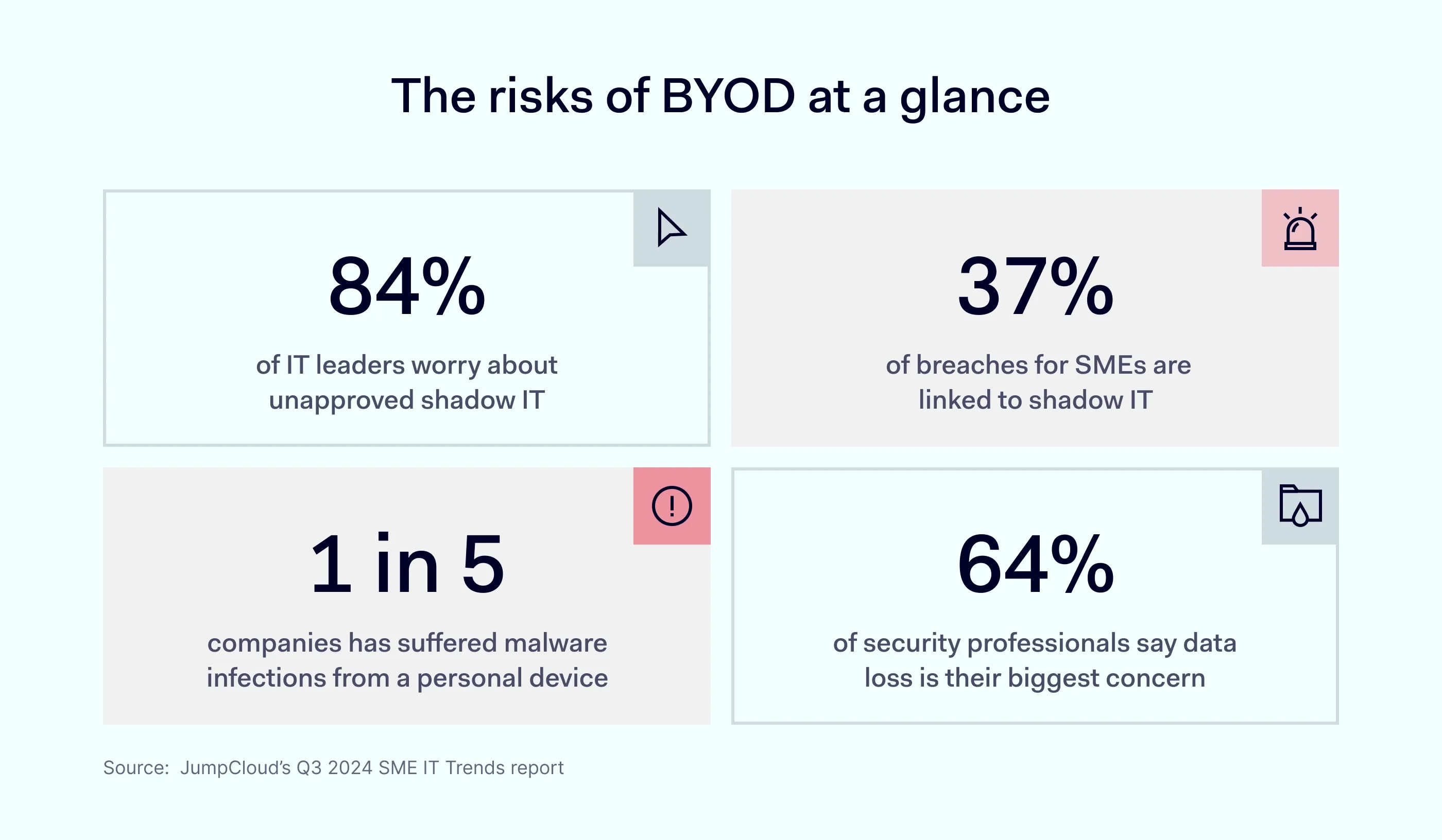
But while BYOD offers more freedom, increases employee productivity, and reduces company hardware costs, the biggest risk is security, with data loss ranking as the #1 concern for businesses. When personal devices are used to access company resources, risks like data leaks, malware, and credential theft become harder to monitor and prevent.
So, the key question for IT leaders is simple: How can companies manage BYOD trends and keep their data safe in 2025? Let’s take a closer look.
BYOD statistics: What you need to know now
The business case for Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) is stronger than ever. It’s a cornerstone of the modern workplace. As remote and hybrid work models are now the new norm, organizations are adopting BYOD to support flexibility, reduce hardware costs, and improve employee experience.
The numbers prove it. Over 80% of organizations now have formal BYOD policies, and 95% allow employees to use their personal devices for work in some capacity.
The motivation for companies is clear. Adopting BYOD brings measurable results. Teams become more productive, employee satisfaction rises, and IT departments cut back on hardware spending.
On average, organizations report a 68% boost in productivity, and over half say workers are more satisfied. Financially, that adds up to $341 saved per employee annually, largely thanks to reduced equipment costs.
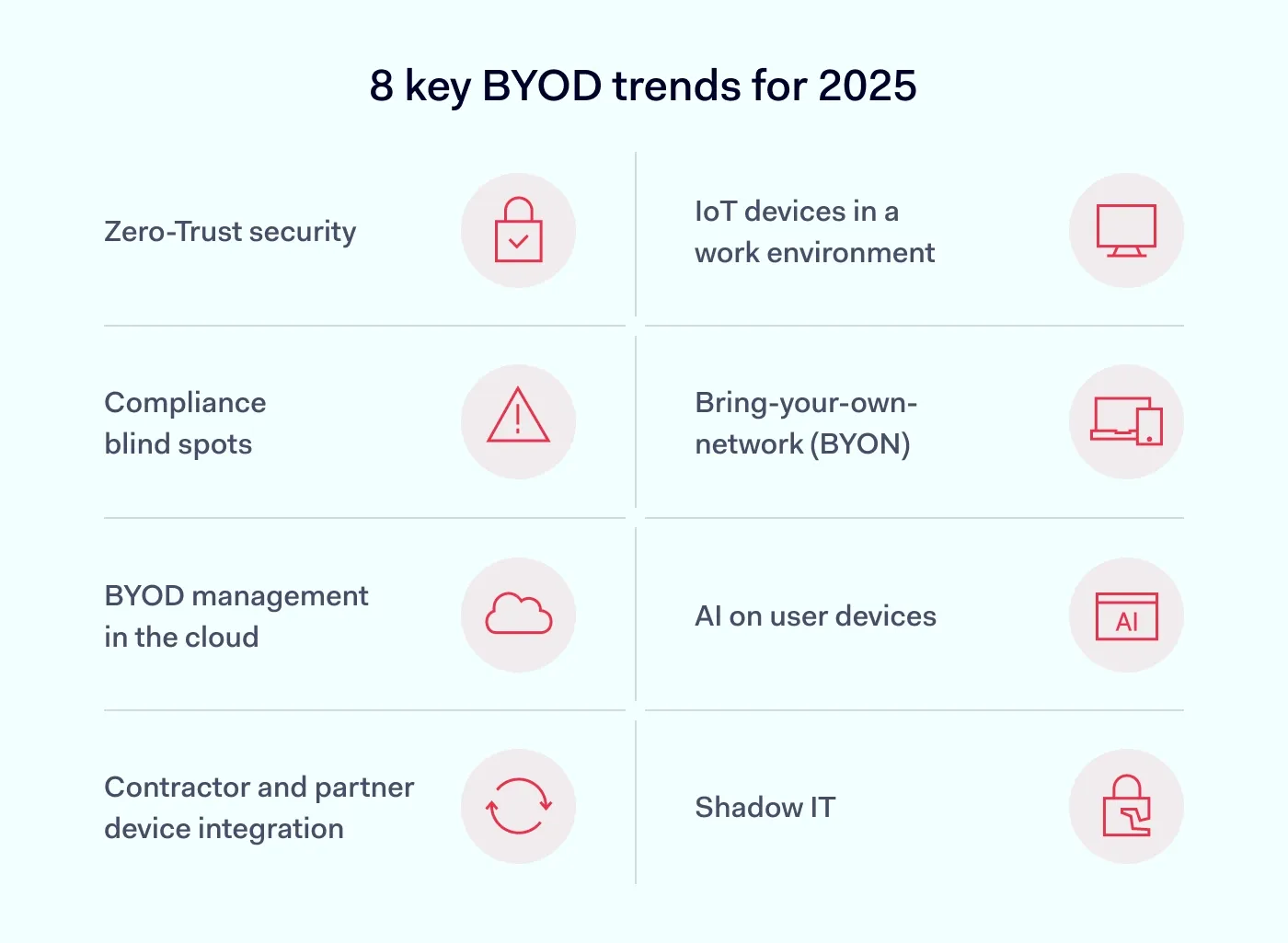
1. Zero-Trust security
Companies are shifting away from trusting devices by default. The new Zero Trust approach assumes every device is a potential threat until proven otherwise. This means using continuous verification and multi-factor authentication (MFA) to ensure company data remains safe, even if a personal device is compromised.
Adopting Zero Trust helps organizations limit access to only the data and systems each user or device needs. This reduces the risk of lateral movement in the network if a breach occurs. It’s an essential strategy to safeguard sensitive information and maintain regulatory compliance.
2. IoT devices in a work environment
Bring-your-own-device is no longer just about phones and laptops. Employees now use personal IoT devices to handle company business. For example, an employee could attend a Zoom call using their smart TV, Google Nest Hub Max, or Amazon Echo Show.
These IoT devices lack enterprise-grade security features and can't be managed through standard mobile device management tools. Hence, they create dangerous blind spots in your defense, leaving sensitive business data exposed through weak authentication and unpatched vulnerabilities.
If your employees use smart, connected IoT devices for work, you must adapt your BYOD procedures to manage these devices alongside traditional ones.
3. Compliance blind spots
As work and home life blend, so do your security perimeters. Employees on personal devices often connect to unsecured networks or bypass security protocols for convenience.
This convenience creates a compliance headache. An employee might unknowingly violate critical data regulations like GDPR or HIPAA simply by storing a customer file on their personal cloud or using a non-approved messaging app.
As a result, a key trend for IT teams is to find a balanced policy that enforces compliance without infringing on employee privacy.
4. Bring-your-own-network (BYON) is on the rise
The trend of "Bring Your Own Network" (BYON) is growing, expanding beyond just devices to include employees using their home internet for work. This practice helps companies manage security risks and control remote connectivity costs associated with BYOD.
As a natural progression from BYOD, BYON creates new challenges and opportunities for IT departments, as companies develop policies for employees to use their personal home networks for work purposes.
5. BYOD management in the cloud
For hybrid and remote teams, the cloud is becoming the central command center for BYOD security. Cloud-based platforms allow IT departments to seamlessly enforce security policies and push critical updates to any personal device, without requiring employee action.
This level of automated control is a proactive defense against ransomware threats that exploit unmanaged BYOD endpoints.
6. AI on user devices
BYOD's future can't escape AI either. With tools like ChatGPT available on iOS and Android, and mobile email apps such as Spark Mail integrating AI features, AI on BYOD endpoints is sure to raise privacy and security concerns over corporate data. Look for Mobile Device Management (MDM) vendors to start taking stronger stances in the future about AI apps on the BYOD endpoints they protect.
7. Contractor and partner device integration
The modern playbook for securing your extended workforce must account for contractor BYOD. Granting deep system access to personal, unmanaged devices is a significant compliance risk.
Organizations are tackling this by shifting the security perimeter from the device to the cloud. While some key contractors may still receive a company-owned laptop, the broader strategy is to use secure cloud platforms as the primary work environment. This ensures that whether a freelancer is on a company laptop or their own, their access to data is tightly controlled.
8. Shadow IT
Shadow IT occurs when employees use unapproved tools or services, such as personal messaging apps or unknown file-sharing platforms. This unregulated use can introduce security risks, especially when employees use their personal smartphones or other mobile devices.
It can lead to hidden vulnerabilities that are hard to detect and manage. Addressing shadow IT in BYOD policies is crucial for maintaining a secure work environment, as it can easily escalate into a major security threat if left unchecked.
4 essential BYOD security tips
Managing security across personal devices can be tricky. To protect your business from cyber threats, here are four essential tips to ensure your BYOD policy is both secure and effective.
1. Use secure messaging systems
Even with strong data protection in secure data centers and endpoint security, your data is still at risk if it’s transferred over an unsecured messaging platform.
If you're using tools like Slack, Microsoft Teams, Zoom, WhatsApp for Business, or other popular messaging systems, use their secure features. For example, with Microsoft Teams, you can enjoy encrypted messaging, video calls, and file transfers, all within one secure platform.
Similarly, Slack offers encryption and advanced security features, ensuring that messages and files are protected both in transit and at rest. Zoom has end-to-end encryption for meetings, and Google Chat offers enterprise-level security for team communication.
Even if you’re not using these enterprise solutions, many messaging tools have built-in security features, like end-to-end encryption and secure file sharing.
2. Train employees on mobile device security
Most employees lack proper cybersecurity training, especially when it comes to mobile devices. Phishing emails affect businesses everywhere, and without the right training, your company could fall victim to a cyber-attack.
Phishing prevention training teaches employees to recognize malicious emails, with interactive guidance and random testing throughout the year. This proactive training is far more effective than relying on software alone to protect your business.
Data breaches cost an average of $4.9 million each, so investing in training is a must to protect your company.
3. Use multi-factor authentication (MFA) everywhere
Strong passwords alone aren’t enough to protect sensitive data. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to verify their identity with something they have (like their phone) and their password.
Most online services offer MFA, even for social media accounts. This makes it much harder for attackers to gain access, even if they steal a password.
Implementing MFA ensures your accounts stay safe, even if a password is compromised.
4. Use an enterprise browser to minimize BYOD security risks
In cases where using personal devices is unavoidable, solutions like the upcoming NordLayer Business Browser can provide a simpler, more secure option.
Instead of downloading and maintaining multiple security apps across personal devices, an enterprise browser secures your company's resources directly within the browser. This solution doesn’t interfere with personal apps or violate privacy regulations, making it less intrusive for remote workers while still safeguarding corporate data.
Secure BYOD with NordLayer
BYOD offers flexibility, but security must come first. NordLayer keeps both personal and employer-provided devices secure, offering safe, seamless access no matter where your team works.
With our network security platform, you can protect access to the internet and your network, and secure your connections, helping your network stay safe 24/7.
Our Business VPN encrypts traffic, supports shared and Virtual Private Gateways, and offers Dedicated IPs in 30+ global locations for fast, secure access.
With Zero Trust access controls, only verified users and compliant devices can connect to our network, ensuring only authorized users can access your company’s resources.
You can also take security a step further with NordLayer’s upcoming Business Browser. It is a new-generation browser designed to help IT mitigate browser-based threats and control how employees access SaaS apps. With granular access settings and data loss prevention features, it offers extra oversight, especially in BYOD environments.
NordLayer’s solutions make BYOD safer, but security depends on regular updates, testing, and strong authentication. To embrace BYOD with fewer risks, combine VPN, ZTNA, and the Enterprise Browser.